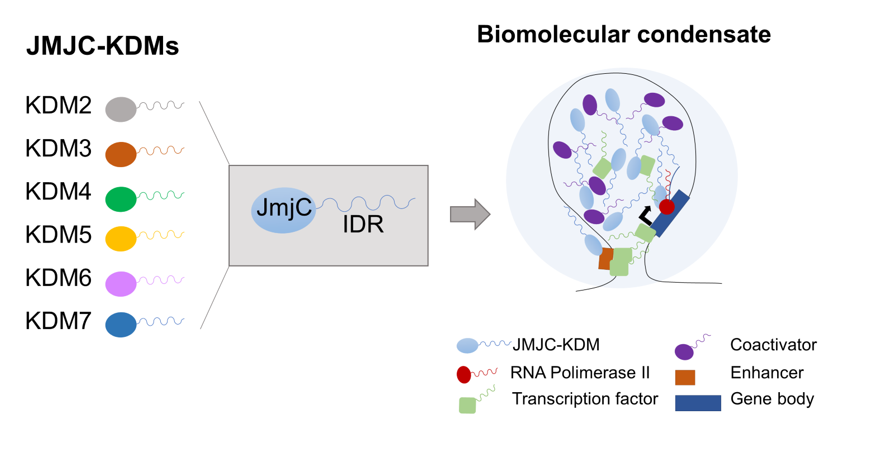
JmjC-family of lysine demethylases (JMJC-KDMs) plays an essential role controlling gene expression and chromatin structure. In most cases, their function has been attributed to the demethylase activity. However, accumulating evidence demonstrates that these proteins play roles distinct from histone demethylation. This raises the possibility that they might share domains that contribute to their functional outcome. Here, we show that the JMJC-KDMs contain low complexity domains as well as intrinsically disordered regions, which in some cases reached 70% of the protein. Our data revealed that PHF2, KDM2A and KDM4B cluster by phase-separation in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, our molecular analysis demonstrated that these domains are important to regulate transcription, suggesting that clustering via phase -separation is a common feature that JMJC-KDMs utilize, in addition to their catalytic activity, to facilitate their functional responses. Our study uncovers a novel potential function for the JMJC-KDM family that sheds light on the mechanisms to achieve the competent concentration of molecules in time and space within the cell nucleus.