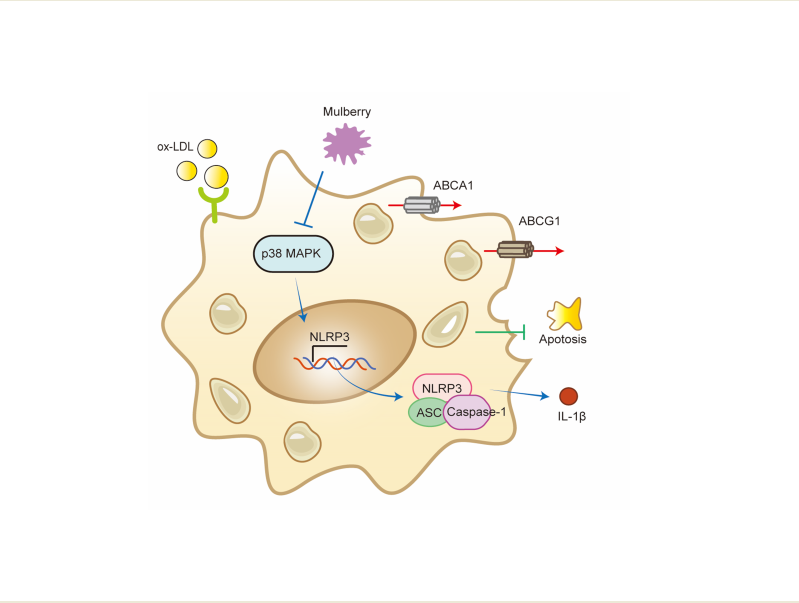
The accumulation of foam cells in arterial intima and the accompanied chronic inflammation are considered major causes of neoatherosclerosis and restenosis. However, both the underlying mechanism and effective treatment for the disease are yet to be uncovered. In this study, we combined transcriptome profiling of restenosis artery tissue and bioinformatic analysis to reveal that NLRP3 inflammasome is markedly upregulated in restenosis and that several restenosis re-lated DEGs are also targets of mulberry extract, a natural dietary supplement used in traditional Chinese medicine to improve liver vitality. Further pathway enrichment analysis identified MAPK signaling pathway to be involved in the inflammatory response of foam cells. Consistently, immunofluorescence microscopy shows co-localization of NLRP3 with CD68+ macrophages. We then evaluated the efficacy of mulberry extract in inhibiting both the formation of foam cells and their inflammatory response. We demonstrated that mulberry extract suppresses the formation of ox-LDL induced foam cells, possibly by upregulating the cholesterol efflux genes ABCA1 and ABCG1 to inhibit intracellular lipid accumulation. In addition, mulberry extract dampens NLRP3 inflammasome activation by stressing the MAPK signaling pathway. Collectively, our mecha-nistic and functional studies unveil the therapeutic value of mulberry extract in neoatherosclerosis and restenosis treatment by regulating lipid metabolism and inflammatory response of foam cells.