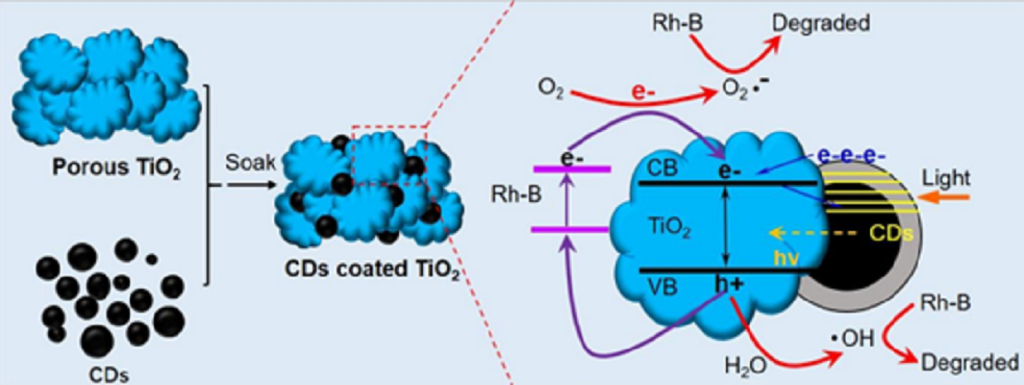
Electron-hole recombination and narrow range utilization of sunlight limit the photocatalytic efficiency of TiO2. We synthesized a carbon dots (CDs) modified TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) with flower-like mesoporous structure, i.e., porous TiO2/CDs nanoflowers. Among such hybrid parti-cles, CDs worked as photosensitizers for the mesoporous TiO2 and enabled the resultant TiO2/CDs nanoflowers with a wide-range light absorption. Rhodamine B (Rh-B) was employed as a model organic pollutant to investigate the photocatalytic activity of the TiO2/CDs nanoflowers. The results demonstrated that the decoration of CDs on both TiO2 nanoflowers and P25 NPs enabled a significant improvement of the photocatalytic degradation efficiency compared with the pristine TiO2. TiO2/CDs nanoflowers with porous structure and larger surface areas than P25 showed a higher efficiency owing to prevent local aggregation of carbon materials. All the results revealed that the introduced CDs and the unique mesoporous structure, large surface areas and loads of pore channels of the prepared TiO2 NPs played important roles in the enhancement of the photocatalytic efficiency of the TiO2/CDs hybrid nanoflowers. Such TiO2/CDs composite NPs also opens a door for photodegradation, photocatalytic water splitting and enhanced solar sun-light as light source.