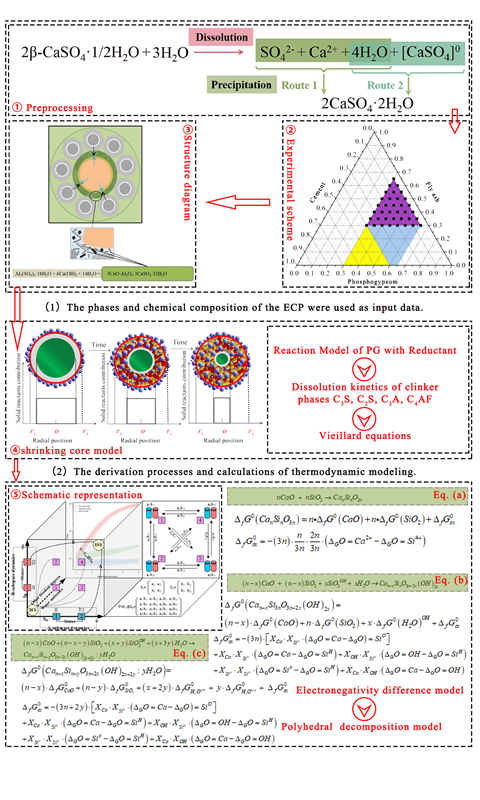
Ecological ternary cements (ECP) were perpared with powders of phosphogypsum (PG), fly ash (FA) and portland cement (PC). The evolution mechanism of the hydration product structure was characterized through macro and micro experiments.The thermodynamic characteristics of solid phase, solid solution phase and aqueous solution in process of hydration about phosphogypsum-fly ash-cement ternary cementitious system were studied based on the Gibbs-free-energy C-S-H thermodynamic model and GEM-Selektor software, and compared with experimental results. The results show that in the hydration reaction the thermodynamic interaction between mineral single-phase and hydration products plays an important role in the spatio-temporal distribution of ions in the cementitious system. The values of CaO、SiO2Hand H2Ohyd gradually increased with the increase of Ca/Si ratio, while the values of CaOext and H2OOH showed a positive proportional relationship, and the values of SiO2H and SiO2 showed an inverse proportional relationship. GEM-Selektor is accurate in the simulation calculation of the total amount of AFt and AFm mineral phases which quantitatively analysis the correlation between C-S-H gels formation and C3S with complex decomposition ion groups.