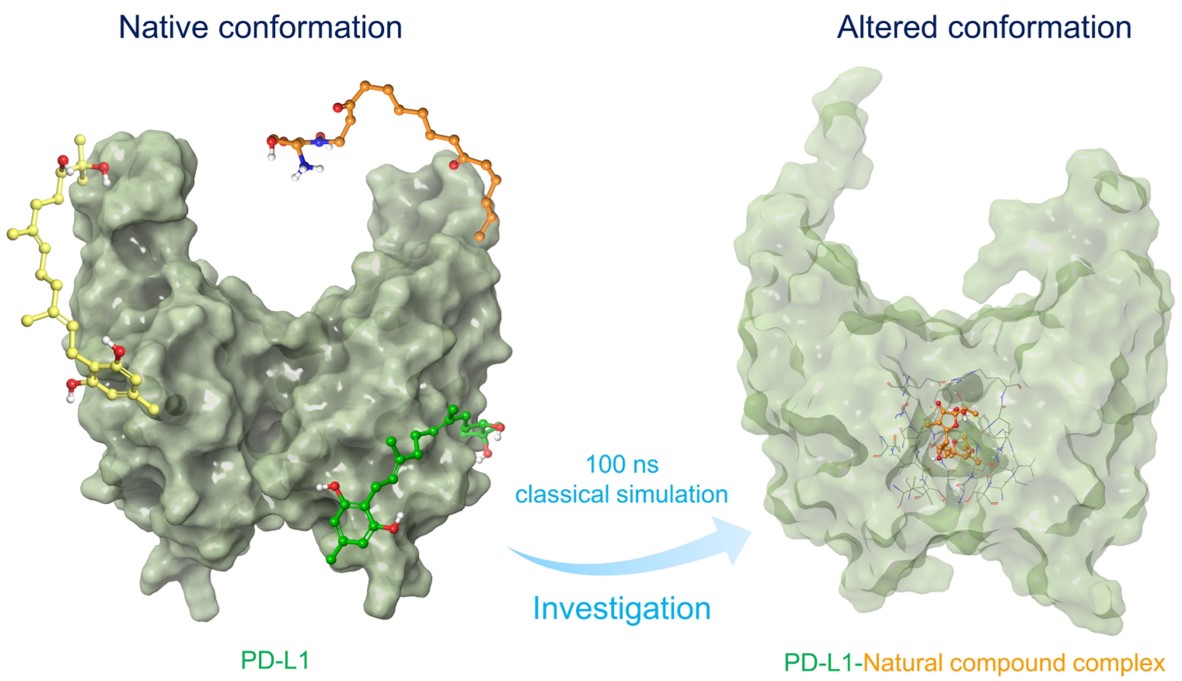
Several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies are approved by FDA against the PD-1/PD-L1 (programmed death-1/programmed death ligand-1) immune checkpoint, which has been a great success in cancer treatment. However, existing therapeutics, including small molecules inhibitors against PD-L1 checkpoint have certain drawbacks such as high cost and drug resistance that challenge the current available anti-PD-L1 therapy. Thereof, this study presents the screening of 32552 compounds from Natural Product Atlas database against PD-L1, including three steps of structure-based virtual screening and binding free energy refinement for the selection of potent PD-L1 inhibitors. Subsequently, five natural compounds, i.e., Neoenactin B1, Actinofuranone I, Cosmosporin, Ganocapenoid A, and 3-[3-hydroxy-4-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)phenyl]-5-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methyldihydrofuran-2(3H)-one, were collected based on the ADMET (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity) profiling and binding free energy (>-70 kcal/mol) for further computational investigation by comparison to co-crystallised ligand, i.e. JQT inhibitor. Based on interaction mapping, explicit 100 ns molecular dynamics simulation, and post binding free energy calculations, all the compounds exhibited intermolecular interactions (hydrogen and hydrophobic) with essential residues and substantial complex stability by comparison to the JQT inhibitor. Collectively, the calculated results advocate the selected natural compounds as the putative potent inhibitors of PD-L1 and, therefore, can be considered for further development of PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitor in cancer immunotherapy.