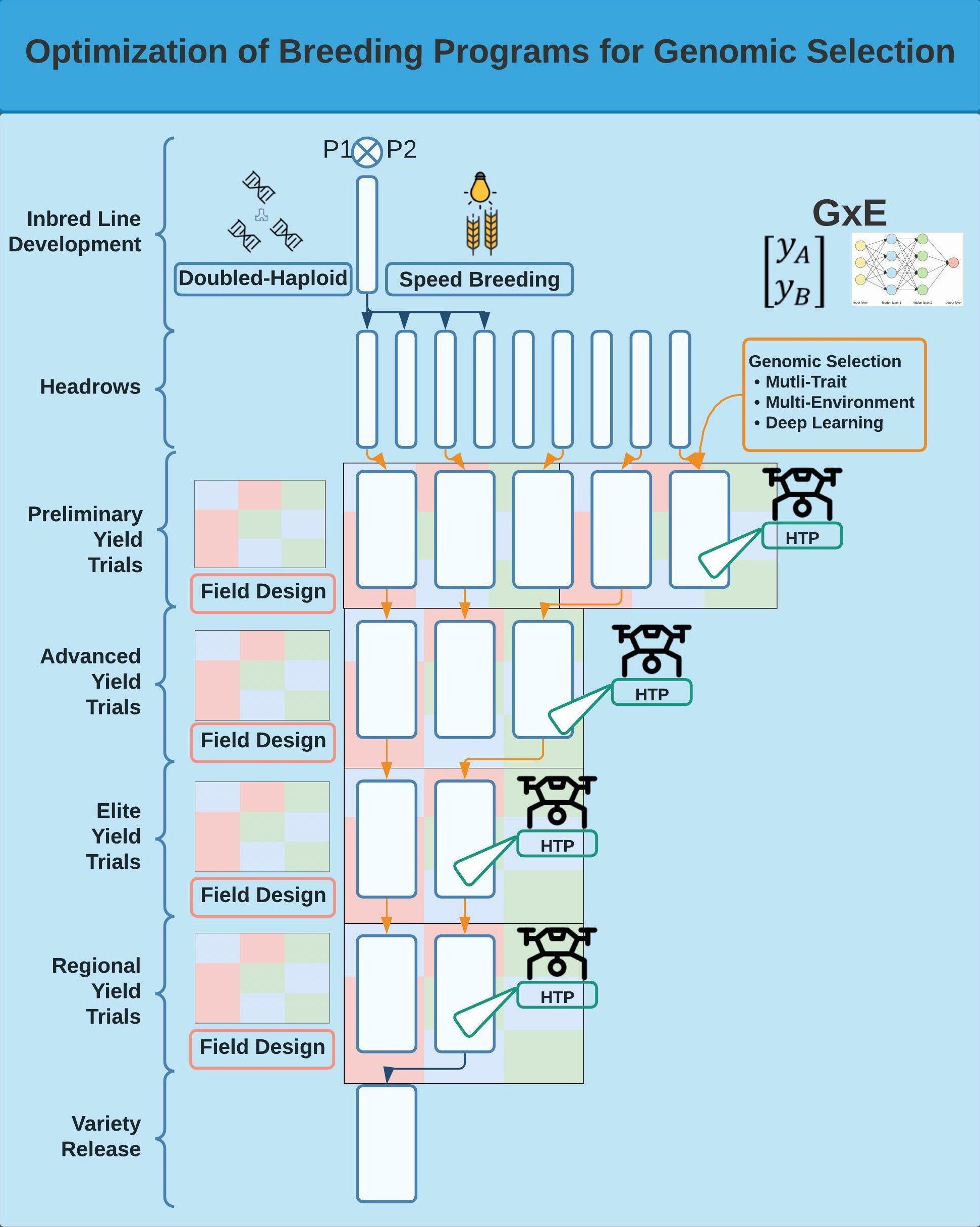
Plant geneticists and breeders have used marker technology since the 1980s in quantitative trait locus (QTL) identification. Marker-assisted selection is effective for large-effect QTL but has been challenging to use with quantitative traits controlled by multiple minor effect alleles. Therefore, genomic selection (GS) was proposed to estimate all markers simultaneously, thereby capturing all their effects. However, breeding programs are still struggling to identify the best strategy to implement it into their programs. Traditional breeding programs need to be optimized to implement GS effectively. This review explores the optimization of breeding programs for variety release based on aspects of the breeder’s equation. Optimizations include reorganizing field designs, training populations, increasing the number of lines evaluated, and leveraging the large amount of genomic and phenotypic data collected across different growing seasons and environments to increase heritability estimates, selection intensity, and selection accuracy. Breeding programs can leverage their phenotypic and genotypic data to maximize genetic gain and selection accuracy through GS methods utilizing multi-trait and, multi-environment models, high-throughput phenotyping, and deep learning approaches. Overall, this review describes various methods that plant breeders can utilize to increase genetic gains and effectively implement GS in breeding .