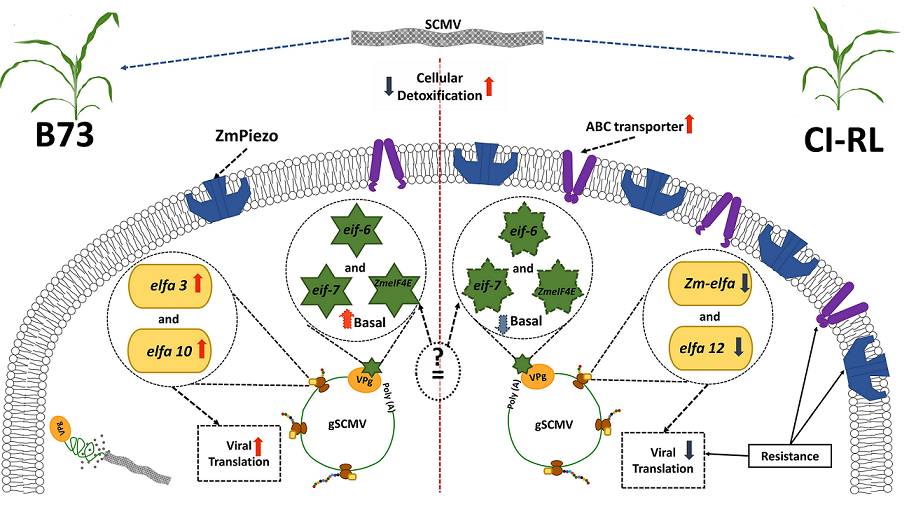
The mosaic disease in maize is caused by Sugarcane mosaic virus (SCMV), a member of the Potyviridae family. The best strategy to cope with viral infections is the use of disease-resistant maize lines. To better understand the resistance response to SCMV, we analyzed differentially expressed genes among a resistant line (CI-RL1), a susceptible line (B73), and the F1 progeny from a cross between both lines using RNA-Seq data. We also analyzed transcript expression pattern clustering to allocate previously reported resistance candidate genes. GO enrichment analysis of biological processes highlighted a strong regulation in ROS detoxification in both the susceptible and resistant lines. The enrichment of cellular components led to the identification of an integral component of the plasma membrane in the RL line. Transcript expression patterns provide evidence of the importance of host translation in virus response, showing the diverse and complex behavior of eIF4E homologs and the presence of eleven eEF1α factors in maize. In addition, we identified two genes putatively implied in long-distance movement: ZmPiezo and ZmPVIP1. Finally, we propose an ABC transporter to be associated with viral resistance.