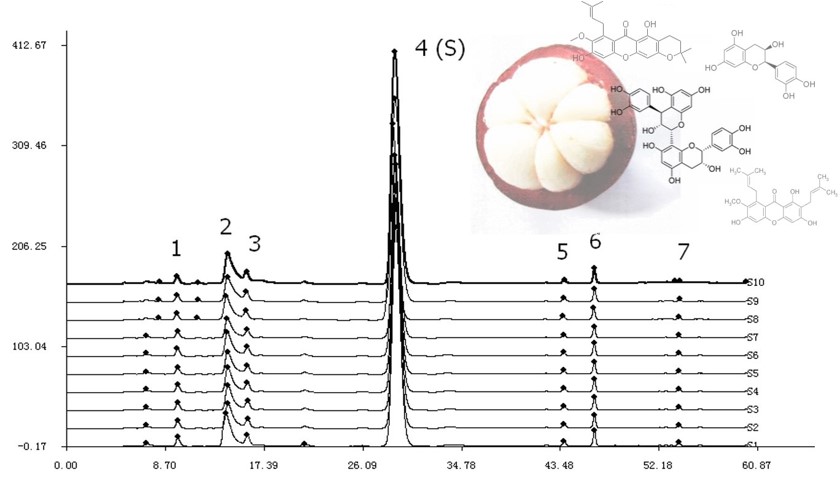
The extracts of Garcinia mangostana L. (mangosteen) are traditionally used for medicinal purposes in Asia. Phenols and xanthones are the two main phenolic compounds with anti-inflammatory activities in the pericarps of mangosteen. A simple and economic reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method has been developed for the simultaneous quantification of phenols (catechin, epicatechin, and procyanidin B2) in mangosteen. The mobile phase was acetonitrile: water (12:88) at 30°C, the flow rate was 1 mL/min, and the detection wavelength was 230 nm. The results showed good linear relationships for catechin from 50-250 ng and for epicatechin and procyanidin B2 from 250-1250 ng. The RP-HPLC fingerprint determination method of total xanthones in mangosteen was also established to provide a new method for quality control of mangosteen extract. The mobile phase was a methanol-water gradient elution at 30°C, the flow rate was 1 mL/min, and the detection wavelength was 320 nm. The similarity of fingerprints of 10 batches of total xanthones was more than 0.90. These methods had good precision, reproducibility, and stability and can be applied in the quality control of mangosteen extracts for medicinal purposes.