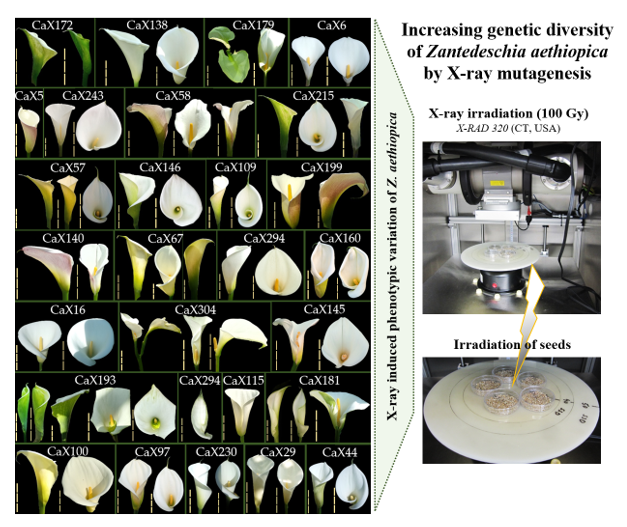
The development of new cultivars is important for the profitability of the floriculture industry. There are a limited number of cultivars of Zantedeschia aethiopica, an iconic ornamental cut flower, garden plant, and potted plant, due to the incompatibility of interspecific crossings within the genus. Most present-day varieties are the result of spontaneous mutations or classical breeding within the species, followed by a long selection process. Breeders are very interested in the development of a time- and cost-effective method for producing new Z. aethiopica cultivars with novel characteristics. Here, Z. aethiopica mutants were generated by treating seeds with 100 Gy of X-ray radiation. The resulting putative mutants were selected based on particular flowering parameters and compared to non-irradiated, control plants. Over two growing seasons, characteristics such as early flowering, flower size and shape, yield and response to soft-rot disease were monitored and considerable variation was observed among the mutated lines. Out of 319 mutants, 20 lines were selected based on their phenotypes and then propagated and further analyzed. Within this group, only two phenotypes displayed at least five improved flowering properties under natural, Mediterranean conditions. The rest displayed two to four desired combinations of flowering traits, some with great commercial potential.