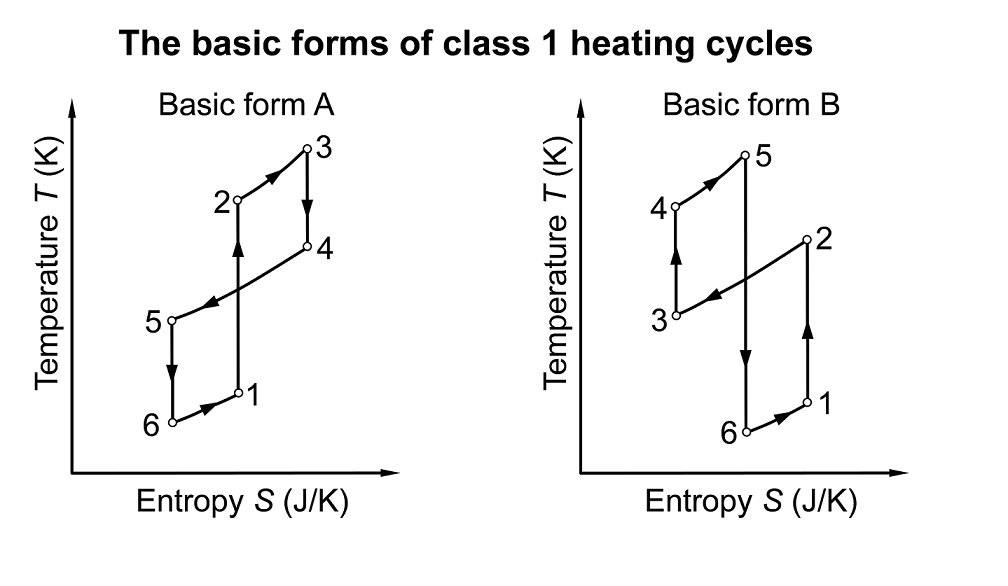
Thermodynamic cycles are not only the core concepts of thermal science, but also key approaches to energy conversion and utilization. So far, power cycles and refrigeration cycles have been the only two general classes of thermodynamic cycles. While diverse types of systems have been developed to perform thermodynamic cycles, no new general classes of thermodynamic cycles have been proposed. Based on the basic principles of thermodynamics, here we propose and analyze a new general class of thermodynamic cycles named class 1 heating cycles (HC-1s). Two basic forms of HC-1s are obtained by connecting six essential thermodynamic processes in the proper order and forming a thermodynamic cycle. HC-1s present the simplest and most general approach to utilizing the temperature difference between a high-temperature heat source and a medium-temperature heat sink to achieve efficient medium-temperature heating and/or low-temperature cooling. HC-1s fill the gaps that have existed since the origin of thermal science, and they will play significant roles in energy conservation and emission reduction.