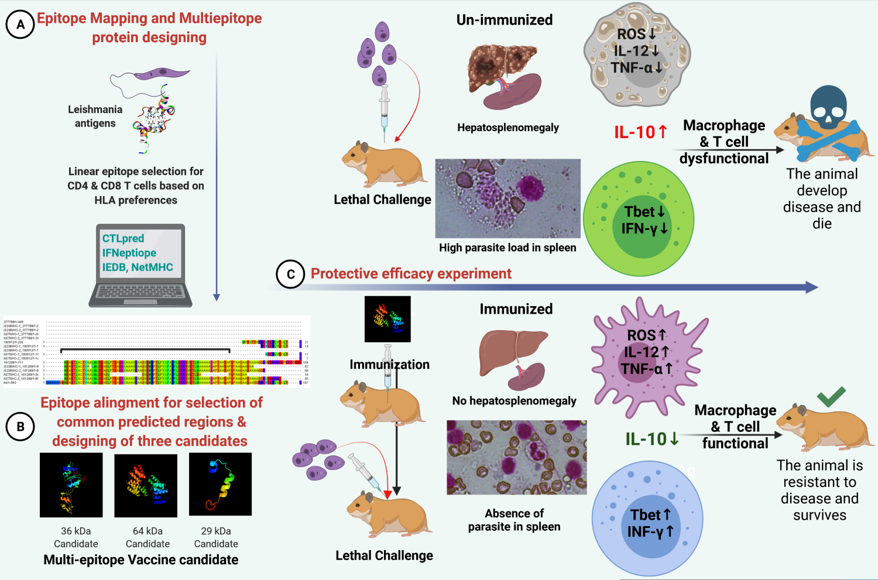
Visceral Leishmaniasis is a neglected tropical disease affecting 12 million people annually. Even in the second decade of the 21st century, it has remained without an effective vaccine for human use. In the current study, we have designed three multiepitope vaccine candidates by the selection of multiple IFN-γ inducing MHC-I and MHC-II binder T-cell specific epitopes from 3 previously identified antigen genes of Leishmania donovani from our lab, by immune-informatic approach using IFNepiotpe, NET-MHC-1 and NET MHC-2 webservers. We have tested the protective potential of these three multiepitope proteins as vaccine in a hamster model of visceral leishmaniasis. The immunization data revealed that the vaccine candidates induced a very high level of Th-1 biased protective immune response in-vivo in a hamster model of experimental visceral Leishmaniasis, with one of the candidates inducing a sterile immunity. The vaccinated animals displayed highly activated monocyte macrophages with the capability of clearing intracellular parasites due to increased respiratory burst. Additionally, these proteins induced activation of polyfunctional T cells secreting INF-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2 in ex-vivo stimulation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, further supporting the protective nature of designed candidates.