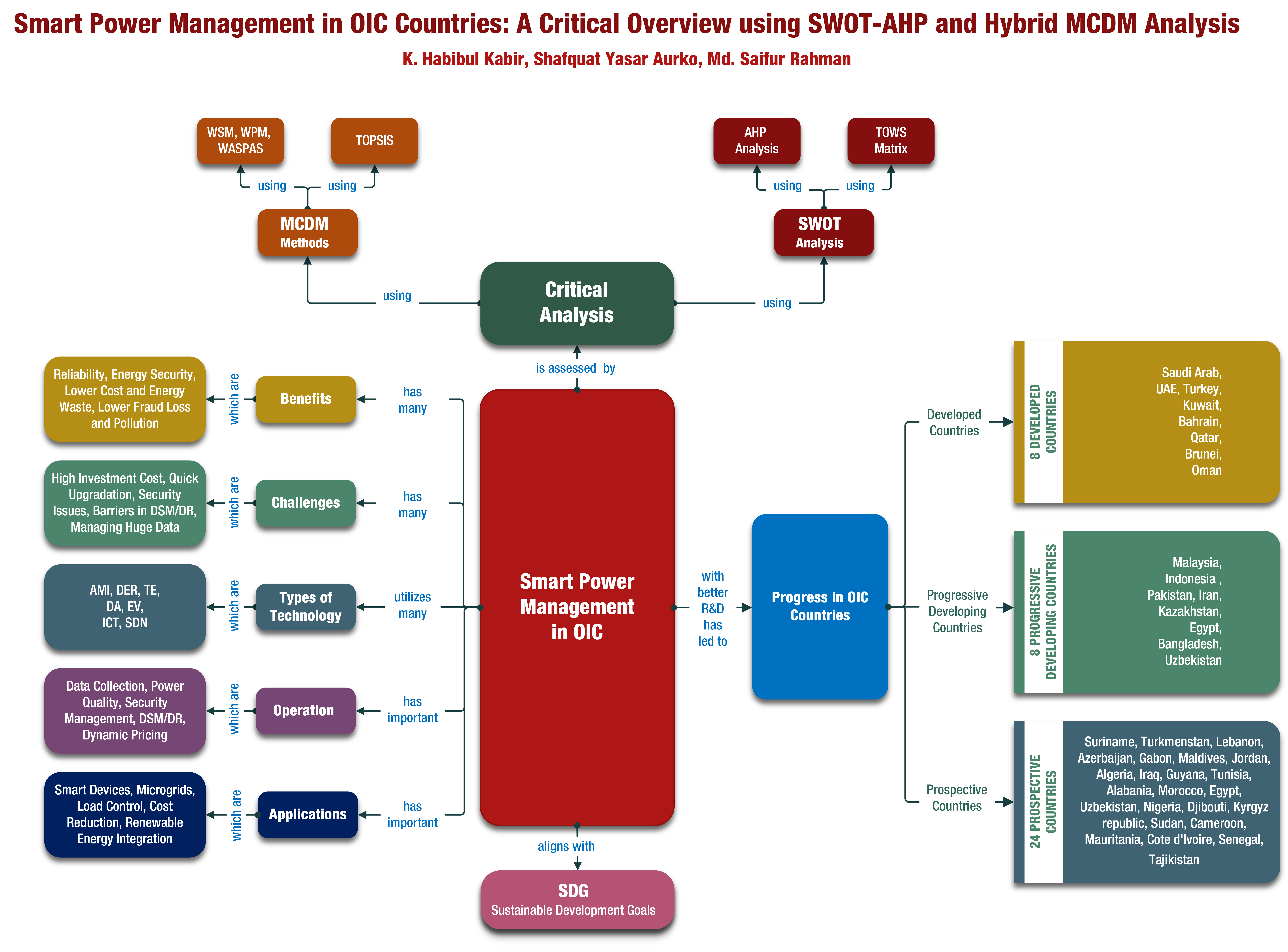
A conventional electrical grid mostly depends on the electrical power generated from fossil fuels. However, the pollutants from fossil fuels are the key factors for adverse climate change. Most of the developed countries of the world have already recognized the fact that the energy mix requires to be diversified by incorporating renewable energy. This is especially relevant for many of the member countries of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), consisting of 57 countries, whose abundance of fossil fuel reserve indicates that much of their electric power is still generated from fossil fuels. In order to integrate renewable energy sources into the hybrid energy mix, an existing conventional grid needs to undergo drastic changes. Alongside this, the population boom in the OIC member countries has caused higher demand for a steady supply of electricity that the conventional grids have long been struggling to cope with. With a view to solving this multifaceted problem, incorporation of the smart power management schemes is indispensable using a smart electrical grid, where information and communications technology is integrated into its major building blocks. This allows advanced applications of a grid, such as the formation of micro-grids, demand-side management, energy storage, high-tech power electronic converters, etc. As the smart grids are being adopted by many developed countries, it is high time for the OIC member countries to pay due attention to this development, if they have not already done so. This paper explains, with special focus on the OIC member countries, the various smart power management technologies, their operations and applications, and the benefits and challenges. Then it goes on to carry out the Strength-Weakness-Opportunity-Threat with Analytical-Heuristic-Procedure (SWOT-AHP) analysis to evaluate its feasibility of incorporation and the underlying strategies appropriate for its implementation. Furthermore, a Hybrid Multi-Criteria-Decision-Making (MCDM) analysis is performed to evaluate the sequence of the emphasis that should be given on each of the technologies from those available for the smart power management initiative. Finally, the study reinforces the stance by drawing parallels from the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) and highlights the importance of the smart grid in line with the global vision of SDG. This paper aims at assisting the decision-makers in implementing smart power management schemes in the OIC member countries, in particular, and other countries of the world, in general.