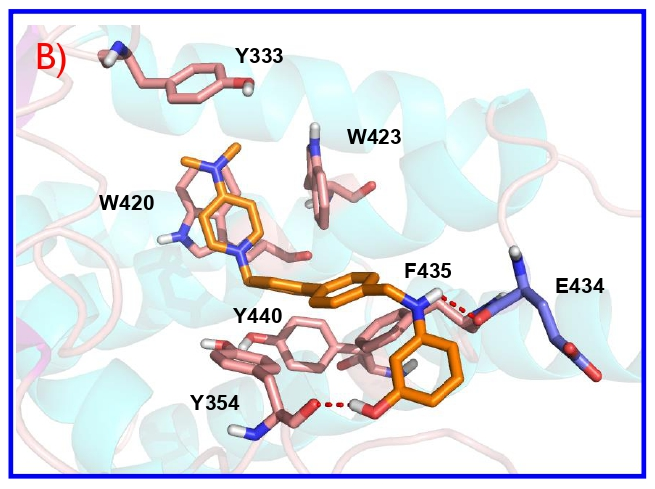
Choline kinase inhibitors are an important class of cytotoxic compounds useful for the treatment of different forms of cancer since aberrant choline metabolism is a feature of neoplastic cells. Here we present the characterization and the structure activity relationship of a series of non-symmetrical choline kinase inhibitors characterized by a 3-aminophenol moiety, bound to 4-(dimethylamino)- or 4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyridinium cationic heads through several linkers. These derivatives were evaluated both for their inhibitory activity on the enzyme and for their antiproliferative activity in a panel of six human tumor cell lines. The compounds with the best inhibitory results were those connected to the linker by the N-atom (4a-h) and these results are supported by docking studies. The compounds with the best antiproliferative results were those connected to the linker by the O-atom (3a-h). On the other hand, as was predictable in both families, the inhibitory effect on the enzyme is greater the shorter the length of the linker, while in tumor cells, lipophilicity and choline uptake inhibition could play a decisive role. Interestingly compounds 3c and 4f, selected for both their ability to inhibit the enzyme and good antiproliferative activity, are endowed with a low toxicity in non-tumoral cells (e.g human peripheral lymphocytes) respect to cancer cells. These compounds were also able to induce to induce apoptosis in Jurkat leukemic cells without causing significative variations of cell cycle. It is worth to mention that these derivatives, beside their inhibitory effect on choline kinase, displayed a modest ability to inhibit choline uptake thus suggesting that this mechanism may also contribute to the observed cytotoxicity.