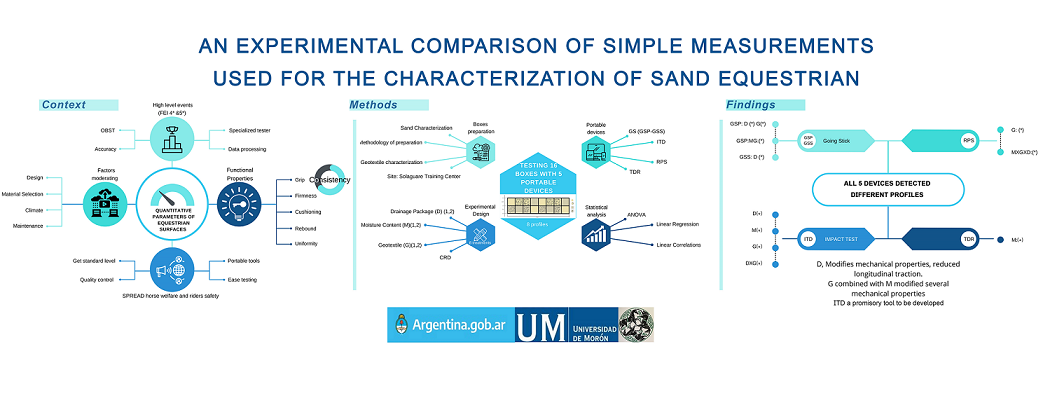
Quantitative measurements of performance parameters has the potential to increase consistency and enhance performance of the surfaces as well as to contribute to the safety of horses and riders. This study investigates how factors known to influence the performance of the surface, incorpo-ration of a drainage package, control of the moisture control, and introduction of a geotextile reinforcement, affect quantitative measurements of arena materials. The measurements are made by using affordable lightweight testing tools which are readily available or easily constructed. Sixteen boxes with arena materials at a consistent depth were tested with the Going Stick (GS), both penetration resistance and shear, the impact test device (ITD), and the rotational peak shear device (RPS). Volumetric moisture content (VMC %) was also tested with time-domain reflectometry (TDR). Results obtained using GS, RPS, ITD, and TDR indicate that the presence of the drainage package, moisture content, and geotextile addition were detected. Alterations due to combinations of treatments could also be detected by GS, ITD, and TDR. While the testing showed some limi-tations of these devices, the potential exists to utilize them for quality control of new installations as well as for the monitoring of maintenance of the surfaces.