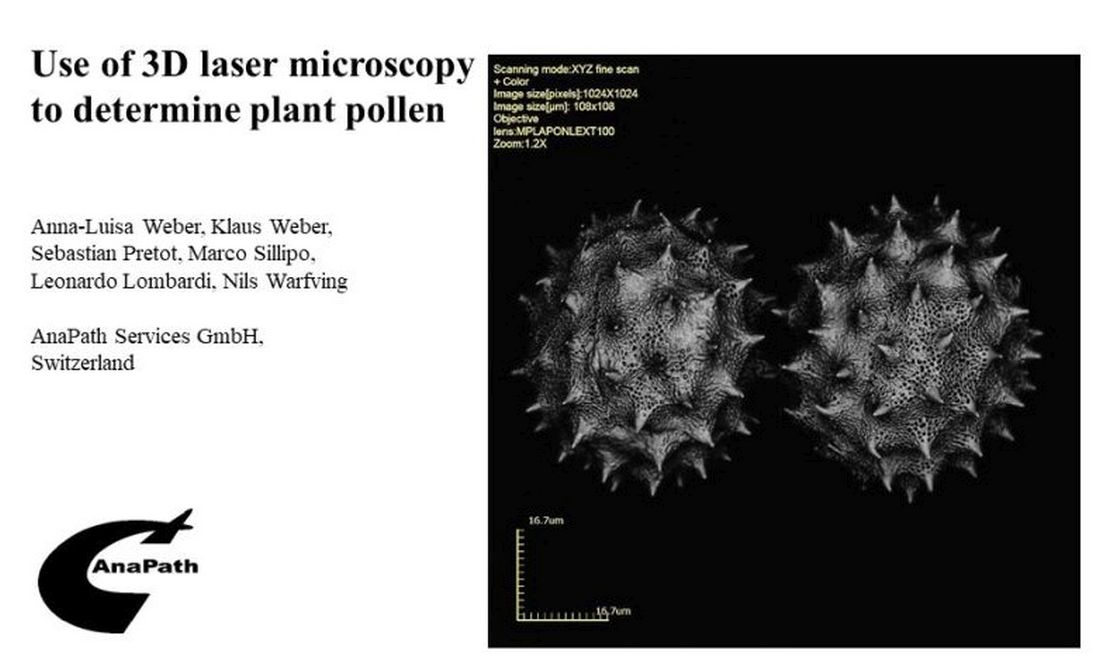
Pollen analysis as a part of palynology deals with the morphological determination of pollen and spores. Different technologies with different resolutions varying from simple light microscopy to highly elaborate electron microscopy are used for the examination, depending on the area of application (e.g. sedimentology, melissopalynology, forensic palynology, etc.). To answer the question of whether laser scanning microscopy (LSM) can replace scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for the determination of pollen species, 168 species were examined using LSM. It was concluded that LSM is both efficient and easy to handle. After preparing the fresh pollen, a 3D laser scan takes 5-10 minutes and unlike using SEM, the pollen does not have to be sputtered or processed. The 3D scans can be measured quickly and easily with the integrated software and there were no observable artifacts. At magnifications up to 8545x, the image quality is comparable to that of a sputtered SEM sample whereas at higher magnifications, the SEM method is superior. Overall, pollen display by LSM is much less time consuming and more cost effective than with the SEM method.