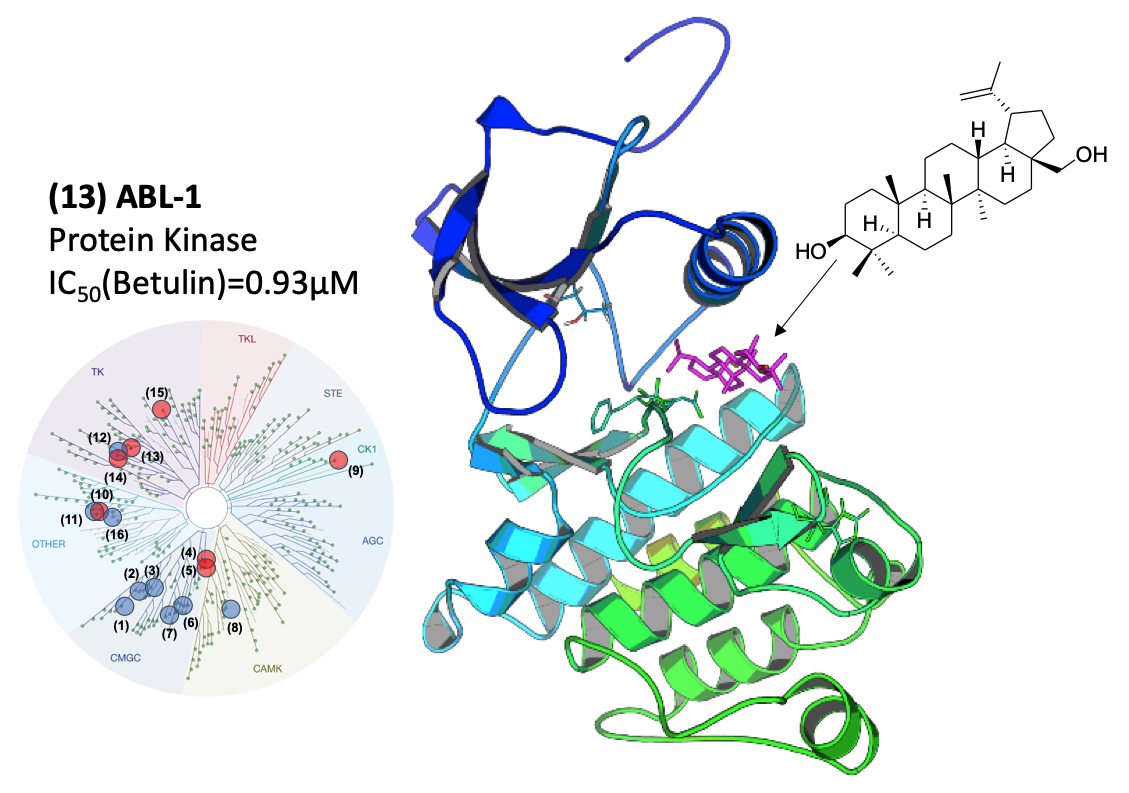
The purpose of this work is to investigate the protein kinase inhibitory activity of constituents from ethyl acetate soluble fraction of Acacia auriculiformis stem bark. Column chromatography, gel filtration and NMR spectroscopy were used to purified and characterized betulin from the extract. Betulin which is a known inducer of apoptosis was screened against a panel of 16 disease-related protein kinases. Betulin was shown to inhibit Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 (ABL1) kinase, casein kinase 1epsilon (CK1epsilon), glycogen synthase kinase 3alpha/β (GSK-3alpha/β), Janus kinase 3 (JAK3), NIMA Related Kinase 6 (NEK6) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 kinase (VEGFR2) and with activity in µM range. The effect of betulin on the cell viability of doxorubicin-resistant K562R chronic myelogenous leukemia cells was then verified to underline its putative use as anti-cancer compound. Betulin was shown to modulate the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway similarly to imatinib mesylate, a well-known inhibitor of ABL1 kinase. The interaction of betulin and ABL1 was studied by molecular docking showing an interaction of the inhibitor with the ATP binding pocket. Altogether, these data demonstrate that betulin is a multi-target inhibitor of protein kinases, an activity that can contribute to the anticancer properties of the natural compound and notably for treatment of leukemia.