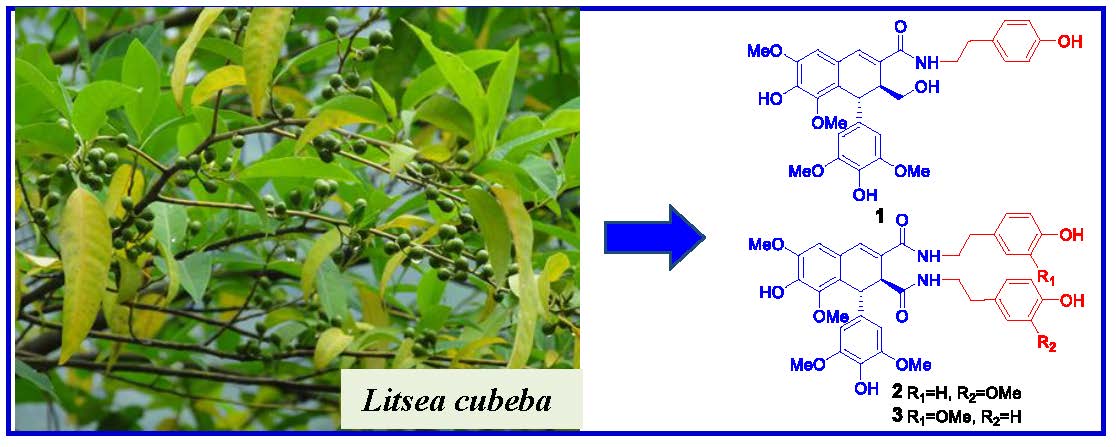
Litsea cubeba, an important medicinal plant, is widely used as traditional Chinese medicine and spice. Using cytotoxicity-guided fractionation, nine new lignans (1-9) and eleven known analogues (10-19) were obtained from the EtOH extract of the twigs of L. cubeba. Their structures were assigned by extensive 1D and 2D NMR experiments, and the absolute configurations were resolved by specific rotation and a combination of experimental and theoretically calculated electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra. In the cytotoxicity assay, 7',9-epoxylignans with feruloyl or cinnamoyl group (7-9, 13 and 14) were selectively cytotoxic against NCI-H1650 cell line, while the dibenzylbutyrolactone lignans (17-19) exerted cytotoxicities against HCT-116 and A2780 cell lines. The results highlighted the structure-activity relationship importance of a feruloyl or a cinnamoyl moiety at C-9′ or/and C-7 ketone in 7',9-epoxylignans. Furthermore, compound 11 was moderate active toward protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) with an IC50 value of 13.5 μM, and compounds 4-6, 11 and 12 displayed inhibitions against LPS-induced NO production in RAW264.7 macrophages, with IC50 values of 46.8, 50.1, 58.6, 47.5, and 66.5 μM, respectively.