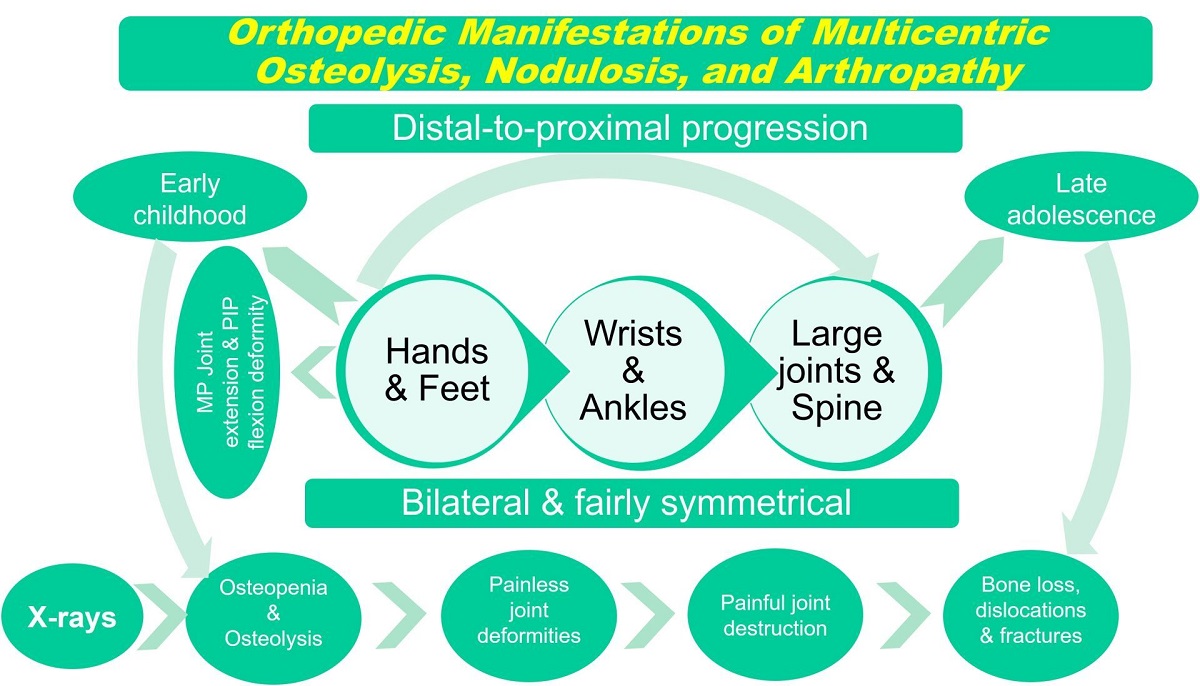
Objectives: Multicentric Osteolysis, Nodulosis, and Arthropathy (MONA) syndrome is a rare genetic skeletal dysplasia. Its diagnosis can be deceptively similar to childhood-onset genetic skeletal dysplasias and juvenile idiopathic arthritis. We aimed to report the syndrome’s clinical and radiologic features with emphasis on skeletal manifestations. And establish relevant phenotype-genotype correlations. Methods: We evaluated two boys, 4-and-7-years-old with MONA syndrome. Both patients had consanguineous parents. We verified the diagnosis by correlating the outcomes of clinical, radiologic and molecular analysis. We specifically evaluated the craniofacial morphology and clinical and radiographic skeletal abnormalities. We contextualized the resultant phenotype-genotype correlations to publications on MONA and its differential diagnosis. Results: Skeletal manifestations were the presenting symptoms and mostly restricted to hands and feet in terms of fixed extension deformity of the metacarpophalangeal and flexion deformity of the interphalangeal joints with extension deformity of big toes. There were arthritic symptoms in the older patient especially of the wrists and minute pathologic fractures. The skeletal radiographs showed osteopenia/dysplastic changes of hands and feet. Both patients had variants in the matrix metalloproteinase2 gene which conformed to phenotype of previously reported literature in one patient while the other had a novel variant which conformed to MONA phenotype. Craniofacial abnormalities were present. However, minimal extra-skeletal manifestations. Conclusion: Overall, there is an emerging distinctive skeletal pattern of involvement in terms of both clinical and radiographic features. This includes age of onset and location of presenting skeletal manifestations, chronological order of joint affection, longitudinal disease progression, specifics of skeletal radiographic pathology and craniofacial features. Nevertheless, physicians are cautioned against differential diagnosis of similar genetic skeletal dysplasias and juvenile idiopathic arthritis.