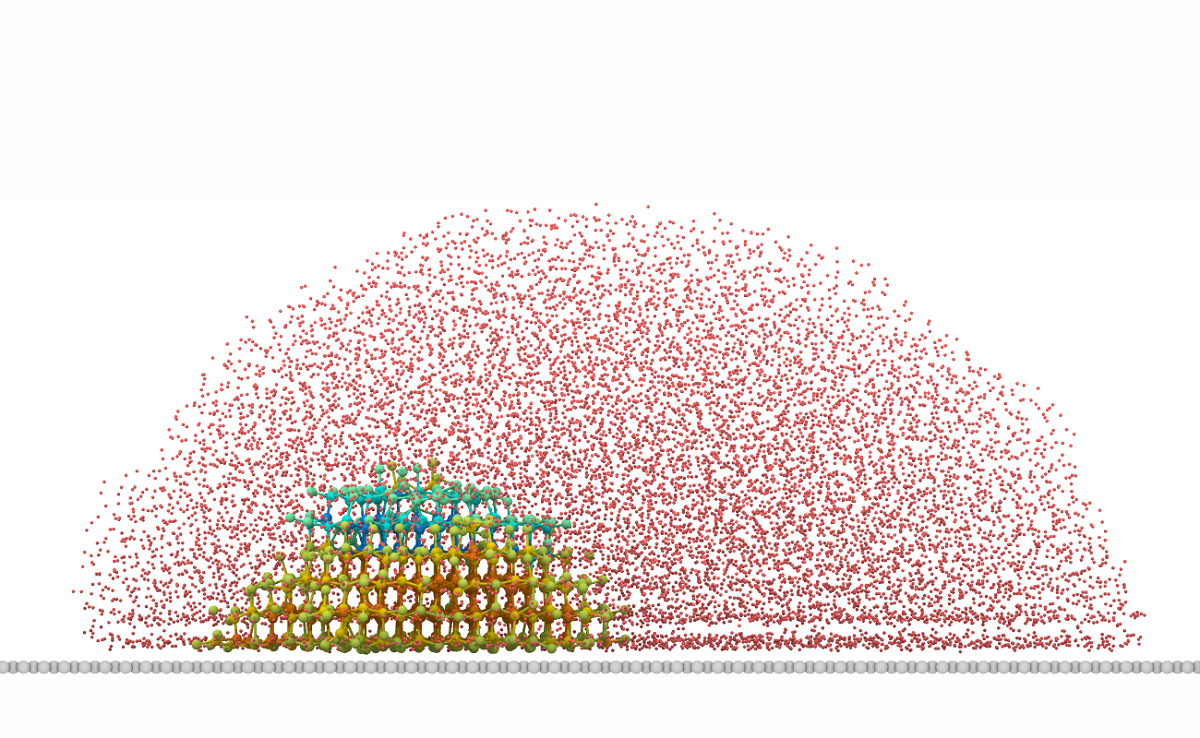
Recently, ice with the stacking disorder structure, consisting of random sequences of cubic ice (Ic) and hexagonal ice (Ih) layers, is reported to be more stable than pure Ih/Ic. While, due to a much lower free energy barrier of heterogeneous nucleation, in practice, the freezing process of water is usually controlled by heterogeneous nucleation which is triggered by an external medium. Herein, molecular dynamic simulations were carried out to explore the polymorph dependence of ice on the lattice structure of substrates. It turns out that, during the nucleation stage, the polymorph of ice nuclei can be severely altered by the graphene substrate, on which the Ih was found to occupy an absolute majority in new-formed ice. This can be attributed to the structure similarity between graphene and basal face of Ih. Besides the nucleation stage, our results suggest that the substrate can not affect the polymorph of ice which is far from the graphene surface. The polymorph selectivity of graphene to Ih will diminish with the growth of ice layer.