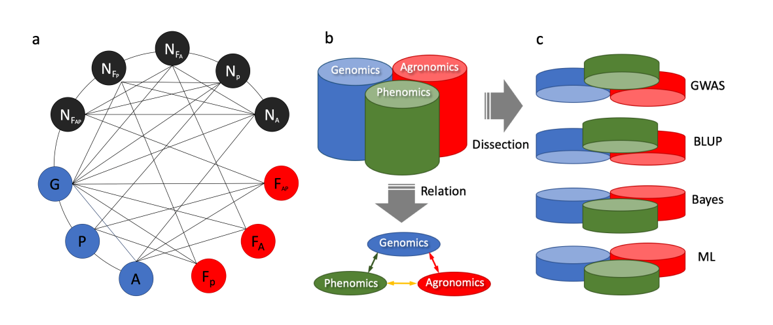
Plant breeding primarily focuses on improving conventional agronomic traits, e.g. yield, quality, and resistance to biotic and abiotic stress; however, genetic improvement methods are being rapidly enhanced through genomics and phenomics. In the Genomics-Phenomics-Agronomics (GPA) paradigm, diverse research approaches have been conducted to bridge any two of these elements, and recently, all of them together. This review first highlights the progress to link i) genomics to agronomics; ii) genomics to phenomics; and iii) phenomics to agronomics. Secondly, the GPA domain is dissected into different layers, each addressing the three elements simultaneously. These dissected layers include genetic dissection through gene mapping using genome-wide association studies and genomic selection using Best Linear Unbiased Prediction, Bayesian approaches, and machine learning. The objective of the review is to help readers to grasp the core developments among the exponentially growing literature in each of these fields. Through this review, the connections among the three elements of the GPA paradigm are coherently integrated toward the prospect of sustainable development of agronomic traits through both genomics and phenomics.