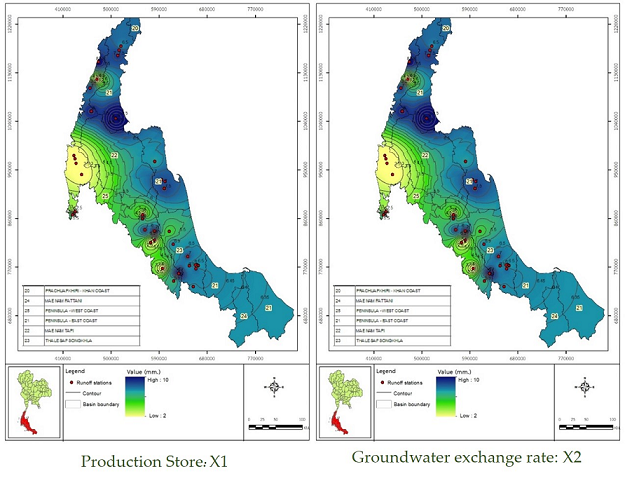
Accurate monthly runoff estimation is fundamental in water resources management, planning, and development, resulting in preventing and reducing water-related problems, such as flooding and drought. This article evaluates the performance of the monthly hydrological rainfall-runoff model, GR2M model, in Thailand's southern basins. The GR2M model requires only two parameters, and no prior research has been reported on its application in this region. The 37 runoff stations, which are distributively located in three sub-watersheds of Thailand's southern region, namely; Thale Sap Songkhla, Peninsular-East Coast, and Peninsular-West Coast, were selected as study cases. The available monthly hydrological data of runoff, rainfall, air temperature from the Royal Irrigation Department (RID) and the Thai Meteorological Department (TMD) were collected and analyzed. Thornthwaite method was utilized for the determination of evapotranspiration. The model's performance was conducted using three statistical indices: Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE), Correlation Coefficient (r), and Overall Index (OPI). The model's calibration results for 37 runoff stations gave the average of NSE, r, and OPI of 0.637, 0.825, and 0.757, and those values for verification of 0.465, 0.750, and 0.639, respectively. It indicated a model's acceptable performance and could apply the GR2M model for determining monthly runoff variation in this region. The spatial distribution of X1 and X2 values was conducted by using IDW method. It was susceptible to the X1 value and X2 value of approximately more than 0.90 gave the higher model's performance.