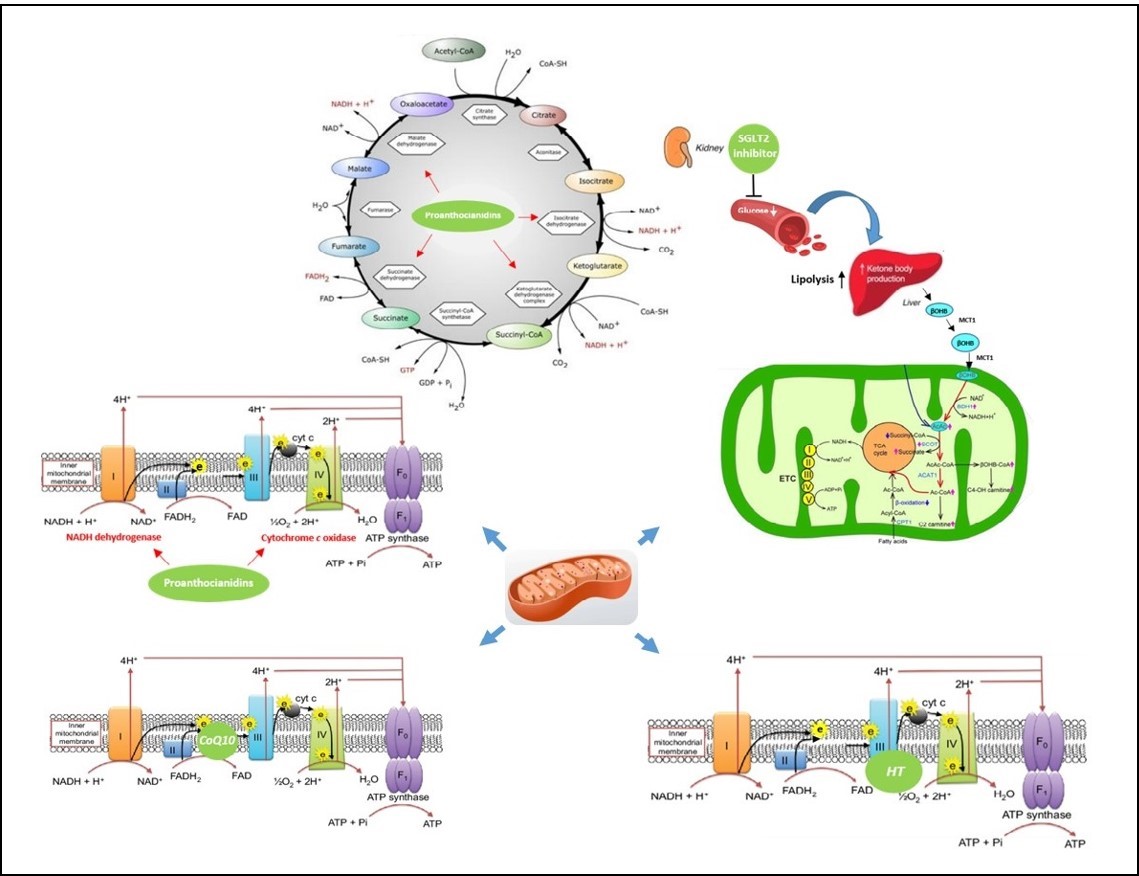
Heart failure (HF) is a disease state which has been shown to affect 1-2% of the global population, being often associated with comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity or hyperlipidaemia which increase the prevalence of the disease, the rate of hospitalization and the mortality. Although recent advances in both pharmacological and non pharmacological approaches have led to significant improvements in clinical outcomes in patients affected by HF, residual unmet needs remain. Treatment of the disease remains unclear particularly related to poorly defined strategies in the early stages of myocardial dysfunction. Nutritional support in patients developing HF and nutraceutical supplementation have recently been shown to may contribute in the protection of the failing myocardium, though their place in the treatment of HF still needs to be better clarified. In this context, the ONUS-HF working group aimed to assess the optimal nutraceutical approach to HF in the early phases of the disease in order to counteract selected pathways which are imbalanced in the failing myocardium. In particular, we reviewed several of the most relevant pathophysiological and molecular changes occurring druing the early stages of myocardial dysfunction. These include mitochondrial and sarcoplasmic reticulum stress, insufficient nitric oxide (NO) release, cardiac stem cell mobilization and imbalanced regulation of metalloproteinases. Several candidates for nutraceutical supplementation in HF, such as CoQ10, grape seed extract, Olea Europea L- related antioxidants, SGLT2 inhibitors-rich apple extract and bergamot polyphenolic fraction have been assessed for their potential contribution to cardiomyocyte prottection. This approach should define the optimal approach for more targeted and successful strategies based on the use of nutraceuticals in HF to be confirmed by means of clinical trials exploring efficacy and safety of these compounds.