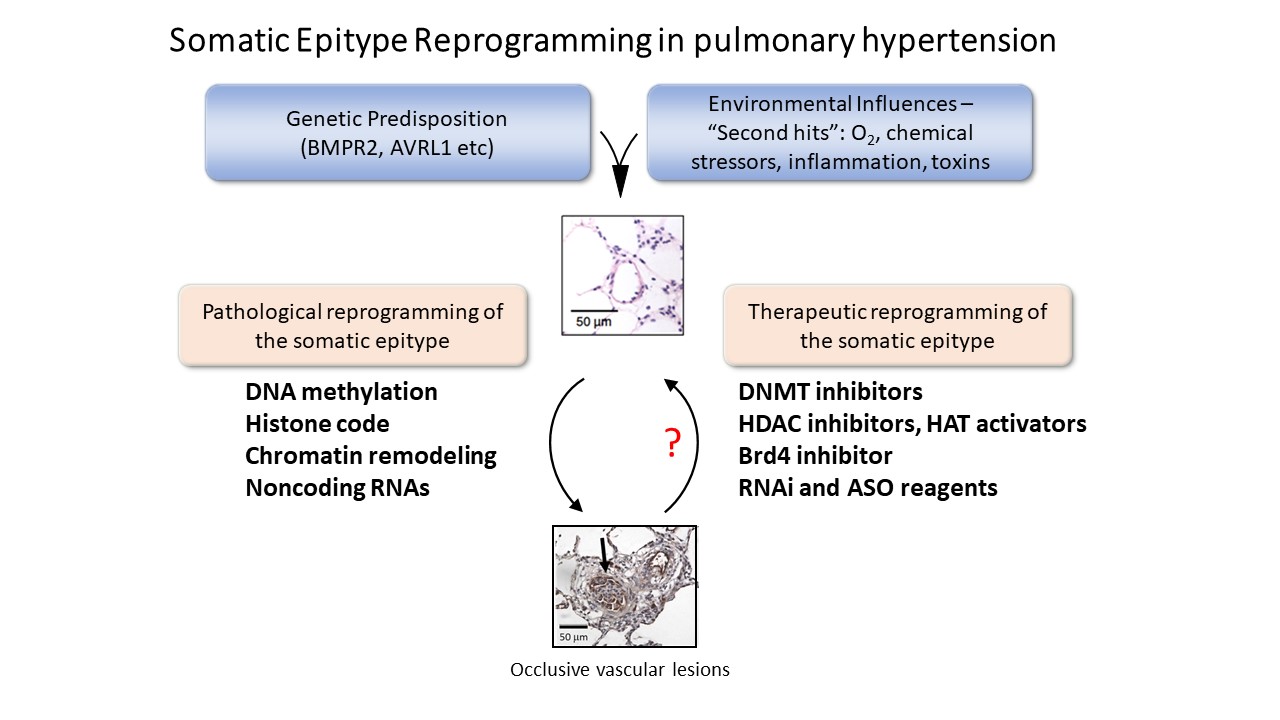
Arterial wall remodeling underlies increased pulmonary vascular resistance and right heart failure in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). None of the established vasodilator drug therapies for PAH prevents or reverses established arterial wall thickening, stiffening and hypercontractility. Therefore, new approaches are needed to achieve long-acting prevention and reversal of occlusive pulmonary vascular remodeling. Several promising new drug classes are emerging from better understanding of pulmonary vascular gene expression programs. In this review potential epigenetic targets for small molecules and oligonucleotides will be described. Most are in preclinical studies aimed at modifying growth of vascular wall cells in vitro or normalizing vascular remodeling in PAH animal models. Initial success with lung-directed delivery of oligonucleotides targeting microRNAs suggests other epigenetic mechanisms might also be suitable drug targets. Those targets include DNA methylation, proteins of the chromatin remodeling machinery and long noncoding RNAs, all of which act as epigenetic regulators of vascular wall structure and function. Progress in testing small molecules and oligonucleotide-based drugs in PAH models is summarized.