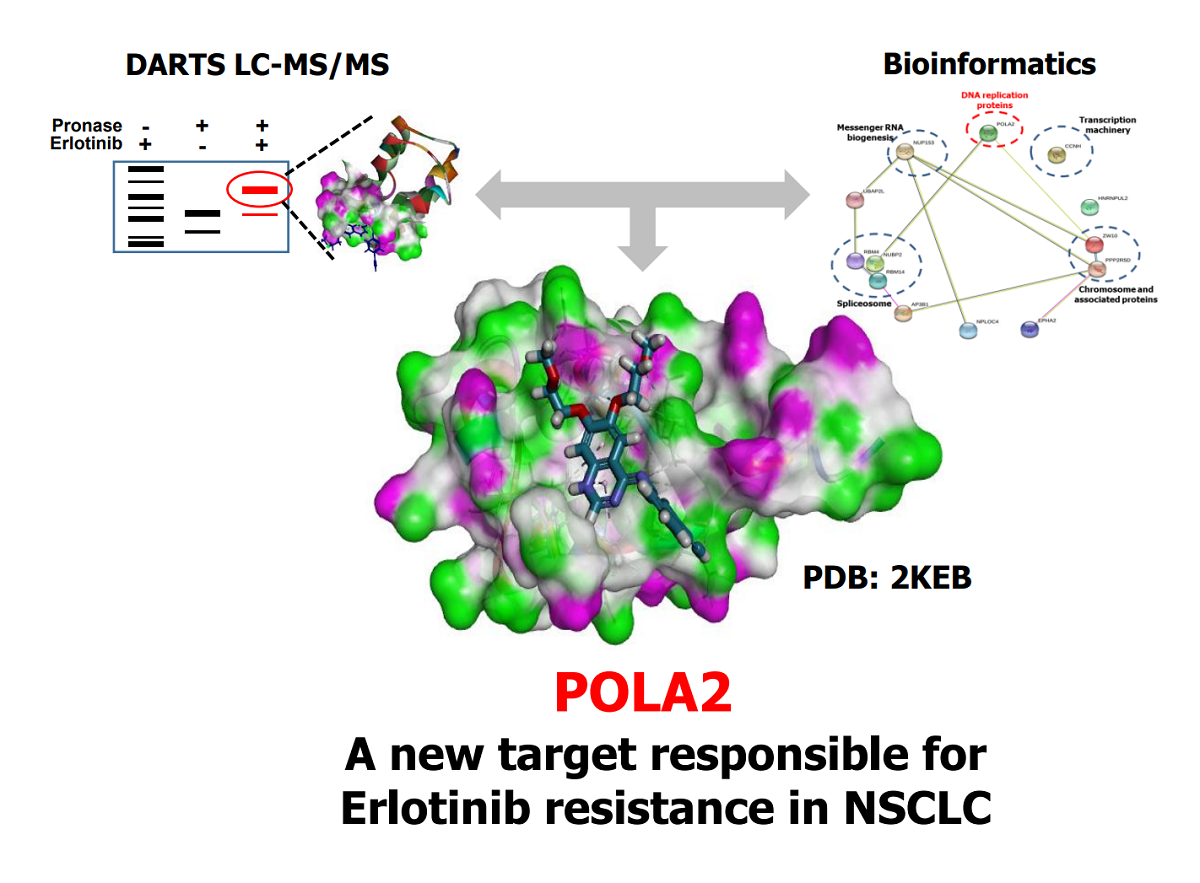
Erlotinib inhibits epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase activity and is used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite its high efficacy, recurrence can occur in patients who become resistant to the drug. To address the underlying mechanism of Erlotinib resistance, we investigated additional mechanisms related to mode-of-drug-action, by multiple protein-binding interactions, besides EGFR by using drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) methods with non-labeled Erlotinib. DNA polymerase alpha subunit B (POLA2) was identified as a new Erlotinib binding protein that was validated by the DARTS platform, complemented with cellular thermal shift assays. Genetic knock-down of POLA2 promoted the anti-proliferative effect of the drug in the Erlotinib-resistant cell line H1299 with high POLA2 expression, whereas overexpression of POLA2 restored anti-proliferative effects in the Erlotinib-sensitive cell line HCC827 with low POLA2 expression. Importantly, POLA2 expression levels in four NSCLC cell lines were positively correlated with anti-proliferative Erlotinib efficacy, verified by bio-statistical analysis (Pearson correlation coefficient, R=0.9886). These results suggest that POLA2 is a novel complementary target protein of Erlotinib, and could clinically provide validity as a surrogate marker for drug resistance in patients with NSCLC.