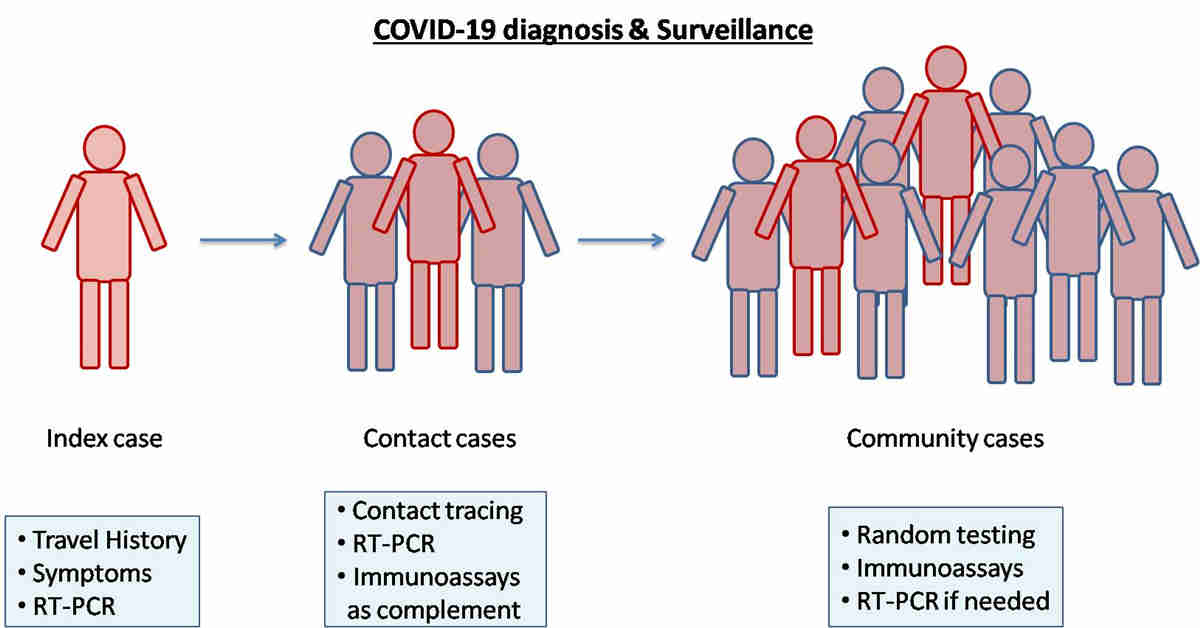
The ongoing pandemic of COVID-19 has not only commenced a global health emergency but agitated various aspects of humanity. During this period of crisis researchers over the world have ramped their efforts to constrain the disease in all possible ways whether it is vaccination, therapy, or diagnosis. Since the spread of the disease has not yet elapsed sharing the ongoing research findings could be the key to disease control and management. An early and efficient diagnosis could leverage the outcome until a successful vaccine is developed. Molecular tests both in-house and commercial kits are preferably being used worldwide in the COVID-19 diagnosis. However, the limitation of high prices and lengthy procedures impede their use for mass testing. Keeping the constant rise of infection in mind search for an alternative test that should be cost-effective, simple, and suitable for large scale testing and surveillance is a need of an hour. One such alternative could be the immunological tests. Therefore, in the last few months deluge of immunological rapid tests has been developed and validated across the globe. The objective of the present review is to share the diagnostic performance of various immunological assays reported so far in SARS-CoV-2 case detection. The article consolidated the studies (published and preprints) related to the serological tests such as chemiluminescence, enzyme-linked and lateral flow-based point-of-care tests in COVID-19 diagnosis and updated the current scenario. This review will hopefully be an add-on in COVID-19 research and will contribute to congregate the evidence for decision-making.