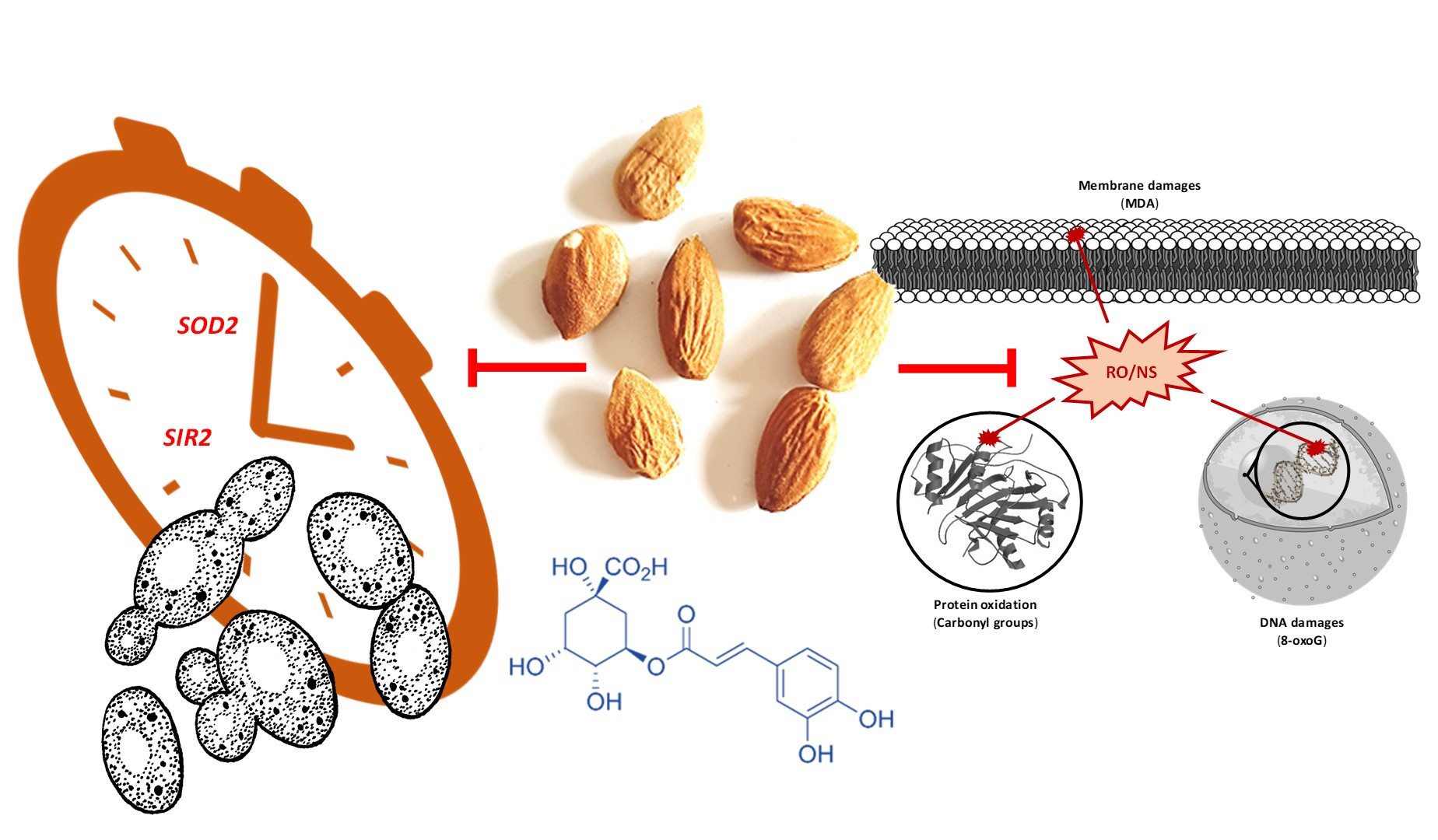
Almond (Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A.Webb) is one of the largest nut crops in the world. Recently, phenolic compounds, mostly stored in almond skin, have been associated with much of the health-promoting behavior associated with their intake. The almond skin enriched fraction obtained from cold-pressed oil residues of the endemic Moroccan Beldi ecotypes is particularly rich in chlorogenic acid. In this study, both almond skin extract (AE) and chlorogenic acid (CHL) supplements, similar to traditional positive control resveratrol, significantly increased the replicative life-span of yeast compared to the untreated group. Our results showed that AE and CHL significantly reduced the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS), most likely due to their ability to maintain mitochondrial function during aging, as indicated by the maintenance of normal mitochondrial membrane potential in treated groups. This may be associated with the observed activation of the anti-oxidative stress response in treated yeast, which results in activation at both gene expression and enzymatic activity levels for SOD2 and SIR2, the latter being an upstream inducer of SOD2 expression. Interestingly, the differential gene expression induction of mitochondrial SOD2 gene at the expense of the cytosolic SOD1 gene confirms the key role of mitochondrial function in this regulation. Furthermore, AE and CHL have contributed to the survival of yeast under UV-C-induced oxidative stress, by reducing the development of ROS / RNS, resulting in a significant reduction in cellular oxidative damage as evidenced by decreased membrane lipid peroxidation, protein carbonyl content and 8-oxo-guanine formation in DNA. Together, these results demonstrate the interest of AE and CHL as new regulators in the replicative life-span and control of the oxidative stress response of yeast.