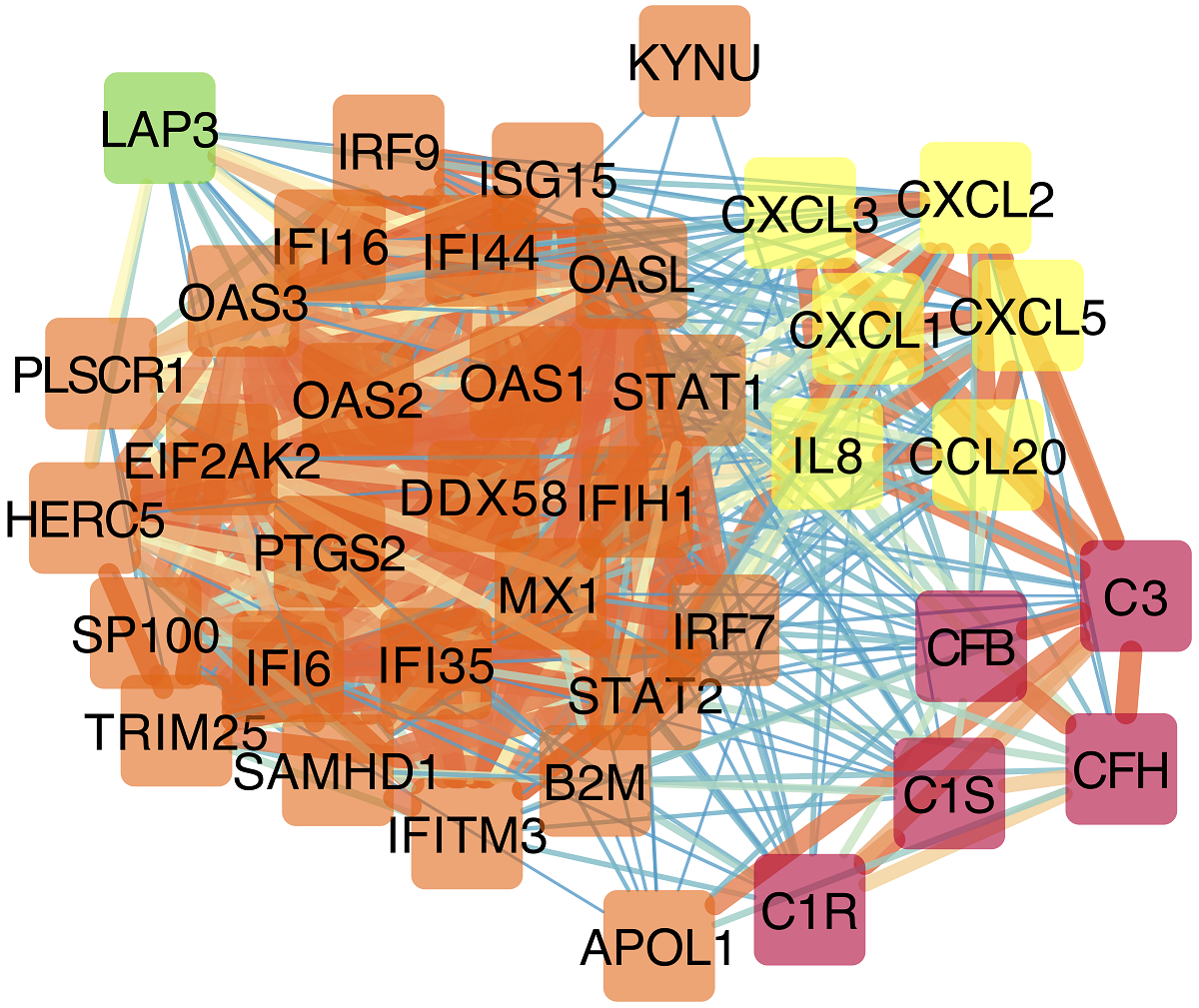
Covid-19 is often related to hyperinflammation that drives lung or multi-organ injury. The immunopathological mechanisms that cause excessive inflammation following SARS-Cov-2 infection are under investigation while different approaches to limit hyperinflammation in affected patients are being proposed. Here, a computational protein-protein interaction network approach was used on recently available data to identify possible Covid-19 inflammatory mechanisms and bioactive genes. First, network analysis of putative SARS-Cov-2 cellular receptors and their directly associated proteins, led to the mining of a robust neutrophil response signature and multiple relevant inflammatory genes. Second, analysis of RNA-seq datasets of lung epithelial cells infected with SARS-Cov-2 revealed that infected cells specifically expressed neutrophil-attracting chemokines, further supporting the likely role of neutrophils in Covid-19 inflammation. Third, analysis of RNA-seq datasets of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from Covid-19 patients, identified neutrophil-specific genes and chemokines. Different immunoregulatory and neutrophil-relevant molecules mined here such as, TNFR, IL8, CXCR1, CXCR2, ADAM10, GPR84, MME-neprilysin, ANPEP and LAP3 are druggable and might be therapeutic targets in efforts to limit SARS-Cov-2 inflammation in severe clinical cases. The role of neutrophils in Covid-19 needs to be studied further.