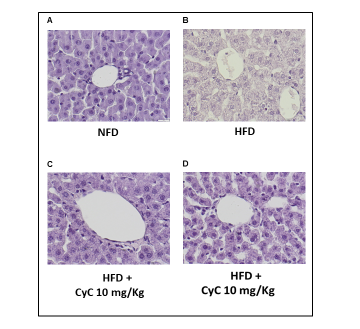
Hyperlipidemia and insulin-resistance are often associated with Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) thereby representing a true issue worldwide, due to increased risk of developing cardiovascular and systemic disorders. Although clear evidence suggests that circulating fatty acids contribute in pathophysiological mechanisms underlying NAFLD and hyperlipidemia, further studies are required for better identify potential beneficial approaches for counteracting such a disease state. Recently, several artichoke extracts have been used for both reducing hyperlipidemia, insulin-resistance and NAFLD, though the mechanism is unclear. Here we used a wild type of Cynara Cardunculus extract (CyC), rich in sesquiterpens and antioxidant active ingredients, in rats fed and High Fat Diet (HFD) compared to Normal Fat Diet (NFD). In particular, in rats fed HFD for four consecutive weeks, we found a significant increase of serum cholesterol, triglyceride and serum glucose. This effect was accompanied by increased body weight and by histopathological features of liver steatosis. The alterations of metabolic parameters found in HFD were antagonised dose-dependently by daily oral supplementation of rats with CyC 10 and 20 mg/Kg over 4 weeks, an effect associated to significant improvement of liver steatosis. The effect of CyC (20 mg/Kg) was also associated to enhanced expression of both OCTN1 and OCTN2 carnitine-linked transporters. Thus, present data suggest a contribution of carnitine system in the protective effect of CyC in diet-induced hyperlipidemia, insulin-resistance and NAFLD.