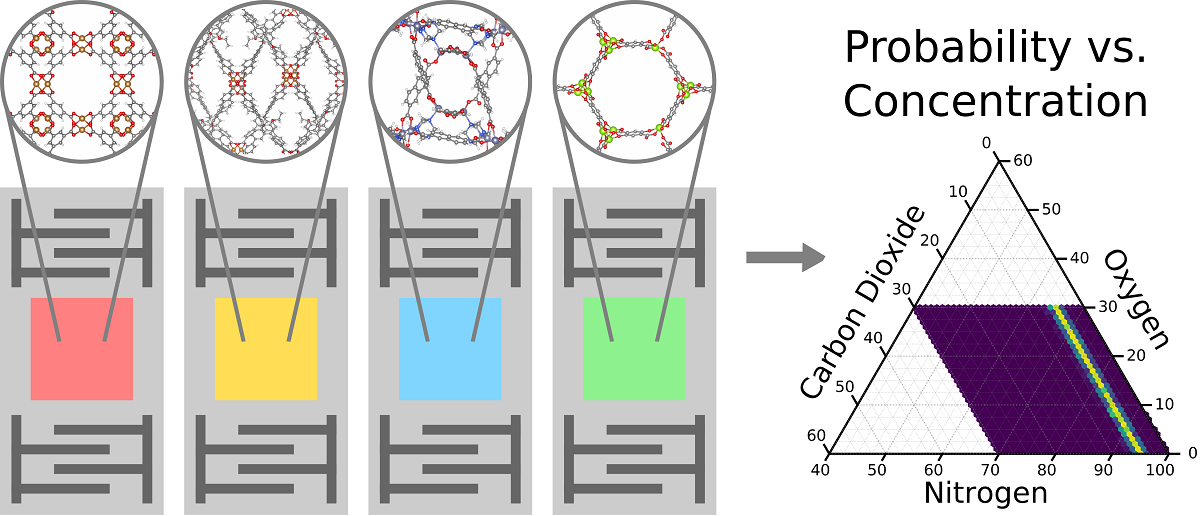
Gas sensor arrays, also known as electronic noses, leverage a diverse set of materials to identify the components of complex gas mixtures. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as promising materials for electronic noses due to their high-surface areas and chemical as well as structural tunability. Using our recently reported genetic algorithm design approach, we examined a set of 50 MOFs and searched through the over 1.125x1015 unique array combinations to identify optimal arrays for the detection of CO2 in air. We found that despite individual MOFs having lower selectivity for O2 or N2 relative to CO2, intelligently selecting the right combinations of MOFs enabled accurate prediction of the concentrations of all components in the mixture (i.e. CO2, O2, N2). We also analyzed the physical properties of the elements in the arrays to develop an intuition for improving array design. Notably, we find that diversity among the surface areas in the MOFs leads to improved sensing. Consistent with the observation, we found that, as one might expect, the best arrays consistently had more structural diversity than the worst arrays.