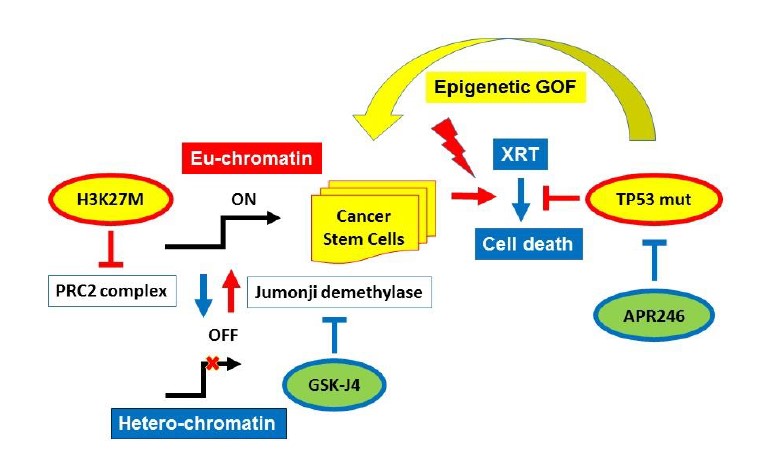
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is an aggressive pediatric brainstem tumor with a 5-year survival of <1%. Up to 80% of DIPG tumors contain a specific K27M mutation in one of two genes encoding histone H3 (H3K27M). Furthermore, p53 mutations found in >70-80% of H3K27M DIPG, and mutant p53 status is associated with a decreased response to radiation treatment and worse overall prognosis. Recent evidence indicates that H3K27M mutation disrupts tri-methylation at H3K27 leading to aberrant gene expression. Jumonji family histone demethylases collaborates with H3K27 mutation in DIPG by erasing H3K27 trimethylation and thus contributing to derepression of genes involved in tumorigenesis. Since the first line treatment for pediatric DIPG is fractionated radiation, we investigated the effects of Jumonji demethylase inhibition with GSK-J4, and mutant p53 targeting/oxidative stress induction with APR-246, on radio-sensitization of human H3K27M DIPG cells. Both APR-246 and GSK-J4 displayed growth inhibitory effects as single agents in H3K27M DIPG cells. Furthermore, both of these agents elicited mild radiosensitizing effects in human DIPG cells (sensitizer enhancement ratios (SERs) of 1.12 and 1.35, respectively; p<0.05). Strikingly, a combination of APR-246 and GSK-J4 displayed a significant enhancement of radiosensitization, with SER of 1.50 (p<0.05) at sub-micro-molar concentrations of the drugs (0.5 μM). The molecular mechanism of the observed radiosensitization appears to involve DNA damage repair deficiency triggered by APR-246/GSK-J4, leading to the induction of apoptotic cell death. Thus, a therapeutic approach of combined targeting of mutant p53, oxidative stress induction, and Jumonji demethylase inhibition with radiation in DIPG warrants further investigation.