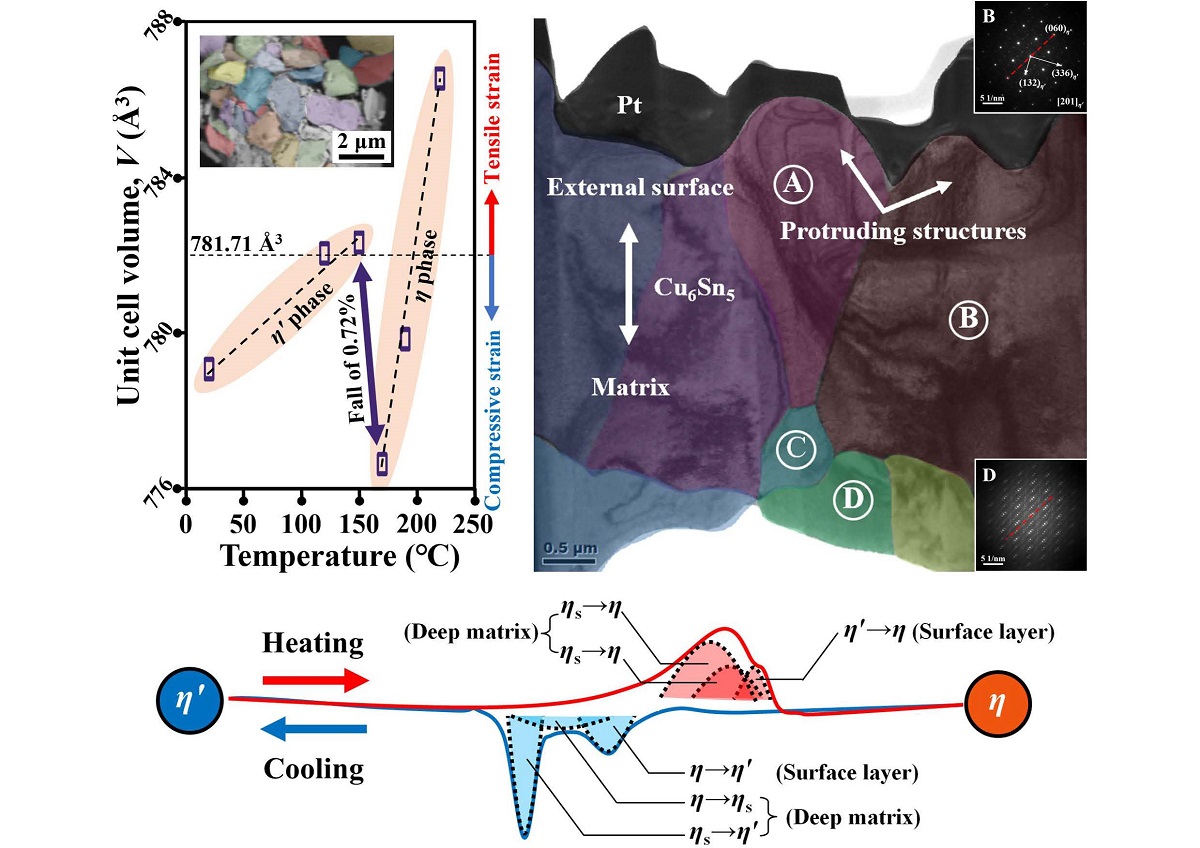
The formation of high-melting-point Cu6Sn5 interconnections is crucial to overcome the collapse of Sn-based micro-bumps and produce reliable intermetallic interconnections in three-dimensional (3D) package. However, because of the multiple reflows in 3D package manufacturing, Cu6Sn5 interconnections will experience the cyclic polymorphic transitions in the solid state. The repeated and abrupt change in the Cu6Sn5 lattice due to the cyclic polymorphic transitions can cause extreme strain oscillations, producing damages at the surface and in the interior of the Cu6Sn5 matrix. Moreover, because of the polymorphic-transition-induced grain splitting and superstructure phase formation, the reliability of Cu6Sn5 interconnections will thus face great challenges in 3D package. In addition, the Cu6Sn5 polymorphic transition is structure-dependent, and the η′↔η polymorphic transition will occur at the surface while the η′↔ηs↔η polymorphic transition will occur in the deep matrix. Our results can provide in-depth understandings of structural evolution and damage mechanism of Cu6Sn5 interconnections in real 3D package manufacturing.