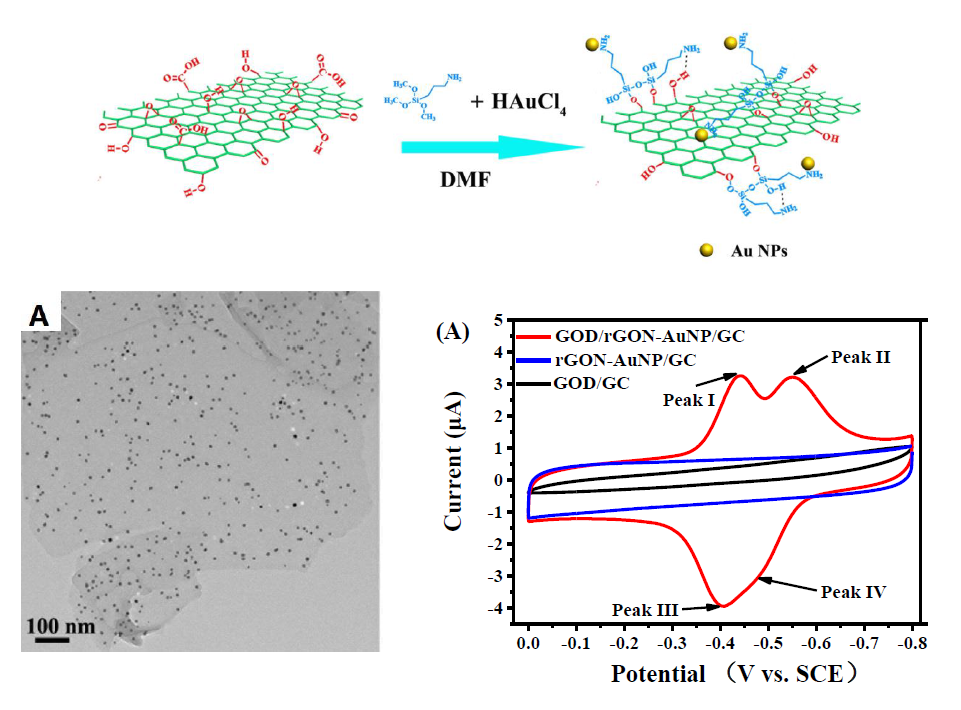
Graphene-based composites have been widely explored for electrode and electrocatalyst materials for electrochemical energy systems. In this paper, a novel composite material of the reduced graphene oxide nanosheets (rGON) with gold nanoparticles (NPs) (rGON-AuNP) is synthesized, and its morphology, structure and composition are characterized by SEM, HRTEM, XRD, EDX, FTIR, Raman, and UV-Vis techniques. To confirm this material’s electrochemical activity, a glucose oxidase (GOD) is chosen as the target reagent to modify the rGON-AuNP layer to form GOD/rGON-AuNP/glassy carbon (GC) electrode. Two pairs of distinguishable redox peaks, corresponding to the redox processes of two different conformational GOD on AuNP, are observed on the cyclic voltammograms of GOD/rGON-AuNP/GC electrode. Both cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy are employed to study the mechanism of direct electron transfer from GOD to GC electrode on the rGON-AuNP layer. In addition, this GOD/rGON-AuNP/GC electrode shows catalytic activity toward glucose oxidation reaction.