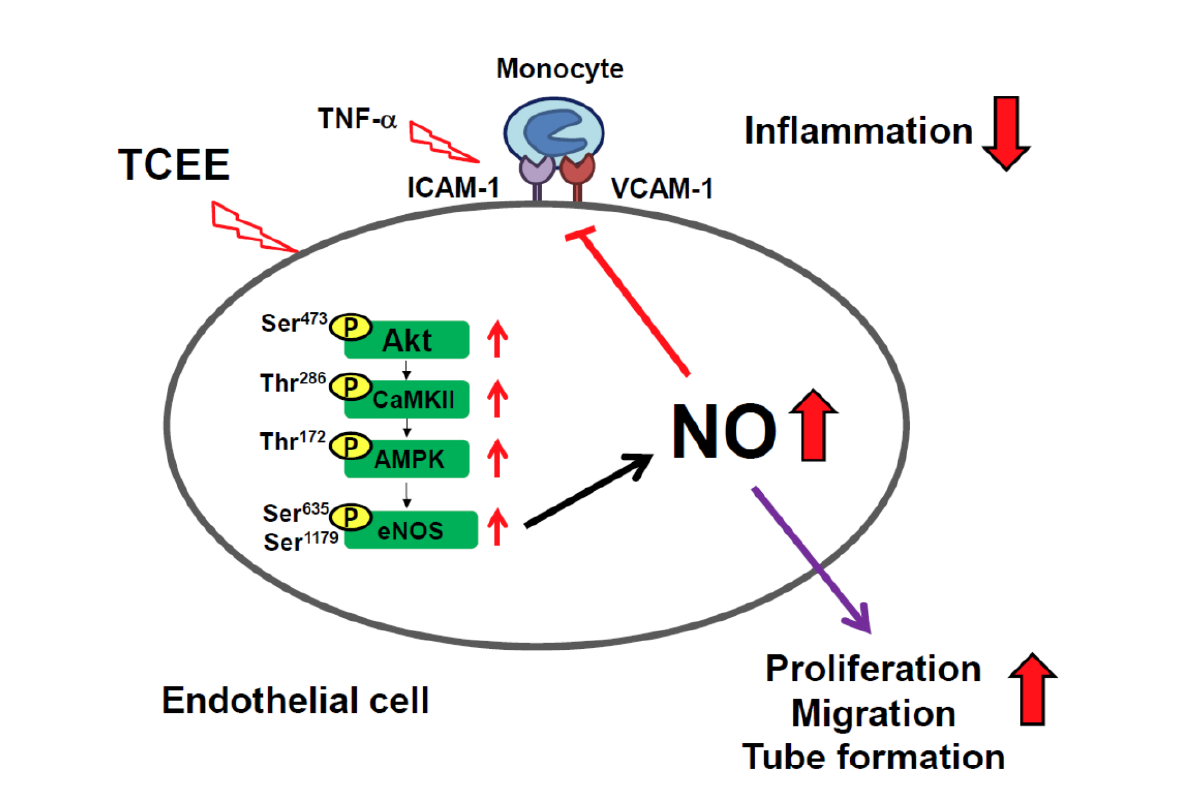
Torenia Concolor Lindley var. formosama Yamazaki ethanolic extract (TCEE) is reported to have anti-inflammatory and anti-obesity properties. However, the effects of TCEE and its underlying mechanisms in the activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) have not yet been investigated. Increasing the endothelium-derived nitric oxide (NO) production has been known to be beneficial against the development of cardiovascular diseases. In this study, we investigated the effect of TCEE on eNOS activation and NO-related endothelial function and inflammation by using in vitro system. In endothelial cells (ECs), TCEE increased NO production in a concentration-dependent a manner without affecting the expression of eNOS. In addition, TCEE increased the phosphorylation of eNOS at serine 635 residue (Ser635) and Ser1179, Akt at Ser473, calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII) at threonine residue 286 (Thr286) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) at Thr172. Moreover, TCEE-induced NO production, and EC proliferation, migration and tube formation were diminished by pretreatment with LY294002 (an Akt inhibitor), KN62 (a CaMKII inhibitor) and compound C (an AMPK inhibitor). Additionally, TCEE attenuated the tumor necrosis factor-α-induced inflammatory response as evidenced by the expression of adhesion molecules in ECs and monocyte adhesion onto ECs. These inflammatory effects of TCEE were abolished by L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (a NOS inhibitor). Collectively, our findings suggest that TCEE confers protection from endothelial dysfunction by activating the Akt/CaMKII/AMPK/eNOS/NO signaling pathway.