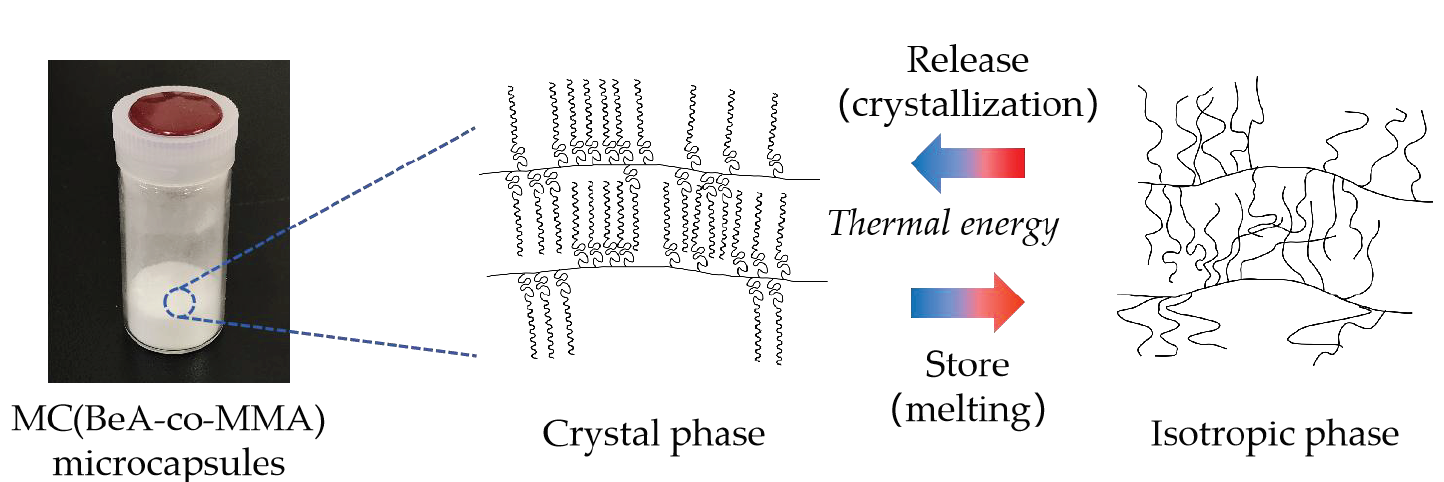
In this paper, we synthesized MC(BeA-co-MMA) copolymer microcapsules through suspension polymerization. The pendent n-behenyl group of BeA is highly crystalline, and it acts as the side-chain in the structure of BeA-co-MMA copolymer. The highly crystalline n-behenyl side-chain provides BeA-co-MMA copolymer thermal-energy-storage capacity. In order to investigate the correlation between thermal properties and crystal structure of BeA-co-MMA copolymer, the effects of monomer ratio, temperature changing and changing rate, as well as synthesis method were discussed. The monomer ratio influenced crystal transition behavior and thermal properties greatly. The DSC results proved that when the monomer ratio of BeA and MMA was 3:1, MC(BeA-co-MMA)3 showed the highest average phase change enthalpy ΔH (105.1 J·g–1). It indicated that the n-behenyl side-chain formed relatively perfect crystal region, which ensured a high energy storage capacity of copolymer. All the DSC and SAXS results proved that the amount of BeA had a strong effect on the thermal-energy-storage capacity of copolymer and the long spacing of crystals, but barely on the crystal lamella. It was found that MMA units worked like defects in the n-behenyl side-chain crystal structure of BeA-co-MMA copolymer. Therefore, a lower fraction of MMA, that is, a higher fraction of BeA contributed to a higher crystallinity of BeA-co-MMA copolymer for providing a better energy storage capacity and thermoregulation property. ST(BeA-co-MMA) copolymer sheets with the same ingredients as microcapsules were also prepared through light-induced polymerization aiming at clarifying the effect of synthesis method. The results proved that synthesis method mainly influenced the copolymer chemical component, but lightly on the crystal packing of n-behenyl side-chain.