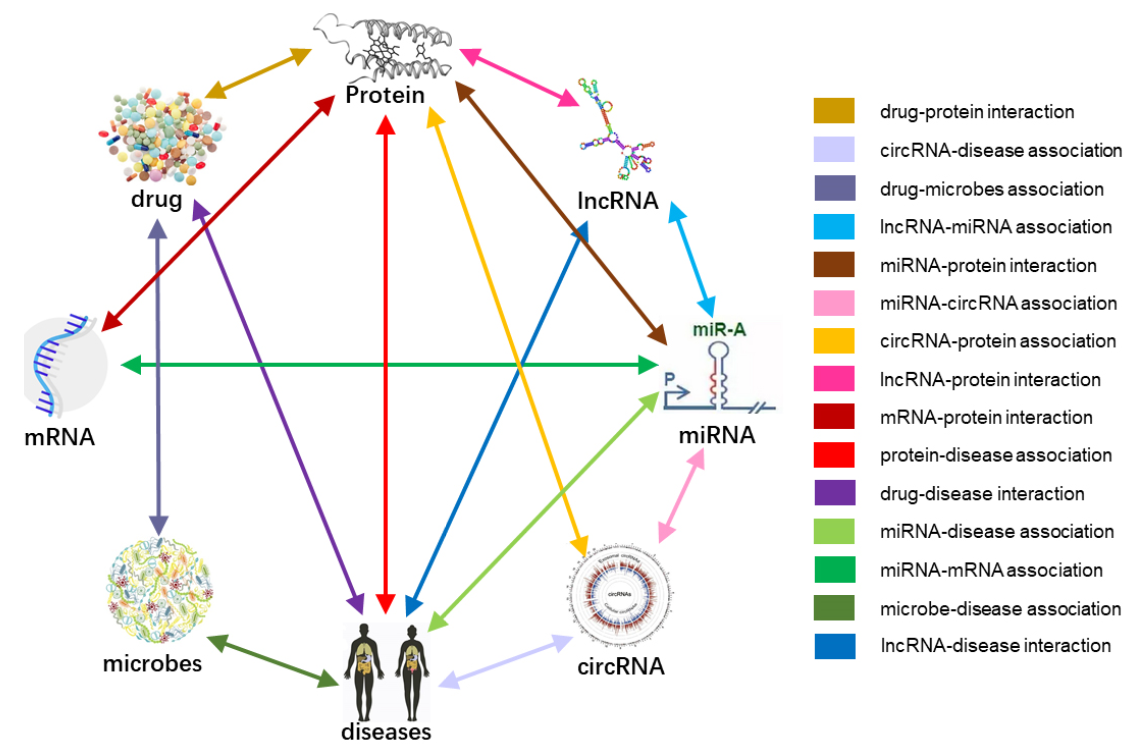
The key issue in the post-genomic era is how to systematically describe the association between small molecule transcripts or translations inside cells. With the rapid development of high-throughput “omics” technologies, the achieved ability to detect and characterize molecules with other molecule targets opens up the possibility of investigating the relationships between different molecules from a global perspective. In this article, a Molecular Associations Network(MAN) is constructed and comprehensively analyzed by integrating the associations among miRNA, lncRNA, protein, drug, and disease, in which any kind of potential associations can be predicted. More specifically, each node in MAN can be represented as a vector by combining two kinds of information including the attributes of the node itself (e.g. sequences of ncRNAs and proteins, semantics of diseases and molecular fingerprints of drugs) and the manner of the node in the complex network (associations with other nodes). Random Forest classifier is trained to classify and predict new interactions or associations between biomolecules. In the experiment, the proposed method achieves a superb performance with 0.9735 AUC in 5-fold cross-validation, which show that the proposed method can provide new insight for exploration of the molecular mechanisms of disease and valuable clues for disease treatment.