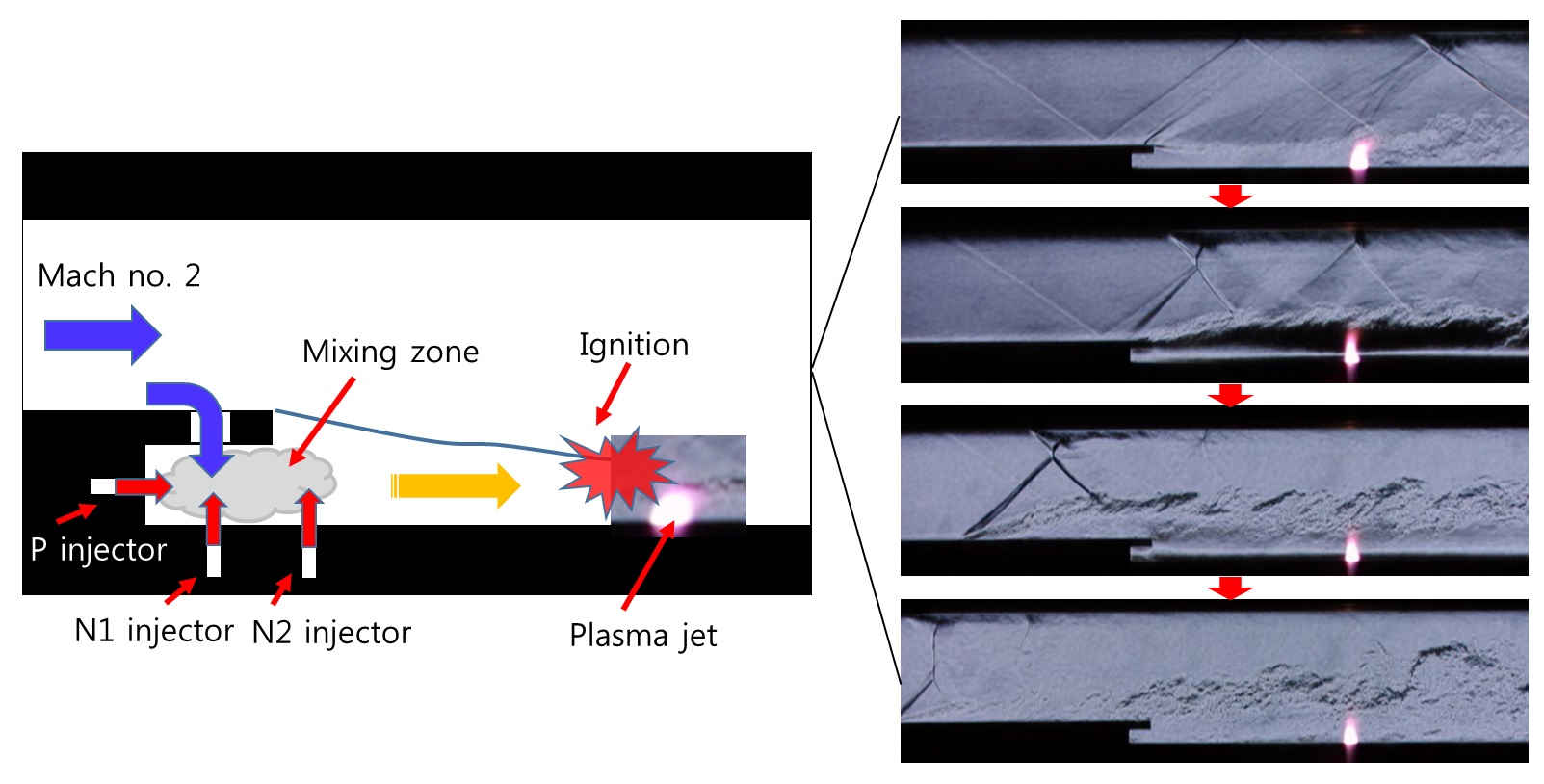
This work focuses on forced combustion with regards to the relationship between vent mixer models and several injection locations in unheated supersonic flow. A plasma jet torch was used to ignite the hydrogen–air mixture in a laboratory-scaled combustor duct. The flow field of the combustion was visualized with pressure and gas-sampling measurements. The vent mixers indicate good dispersion characteristics of the mixture for both parallel and normal 1 injections. However, forced combustion is dominantly governed by the injection rate toward the plasma jet (hot source) because the combustible region is restricted under the cold main flow. For this reason, the parallel injection, which provides the hydrogen–air mixture directly toward the plasma jet, shows good combustion performance. The normal 1 injection interacted with the vent mixers and shows slightly good combustion performance. Lastly, the normal 2 injection is little affected by the vent mixers and has poor combustion performance.