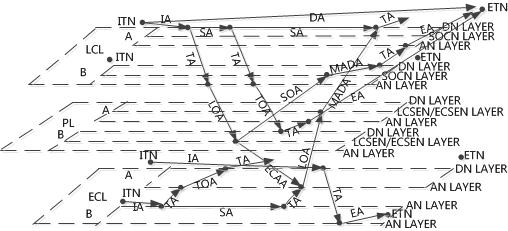
In this paper, the physical station of space network was extended in time dimension by combining the train diagram information and station technical operation standard time. At the same time, the topology of railway space-time network which considered the secondary operation process of train was constructed and an improved A* algorithm based on car flow routing was proposed to generate feasible path sets. On this basis, a dynamic car flow organization optimization model was built to simulate the railway car flow organization process under abnormal conditions, and the results of solving the model could be used to obtain the real-time quantity of cars at each station.This paper can identify the dynamic bottleneck by comparing the real-time quantity of cars with the maximum quantity of cars at the station. Finally, the feasibility of this method was analyzed and verified by a case.