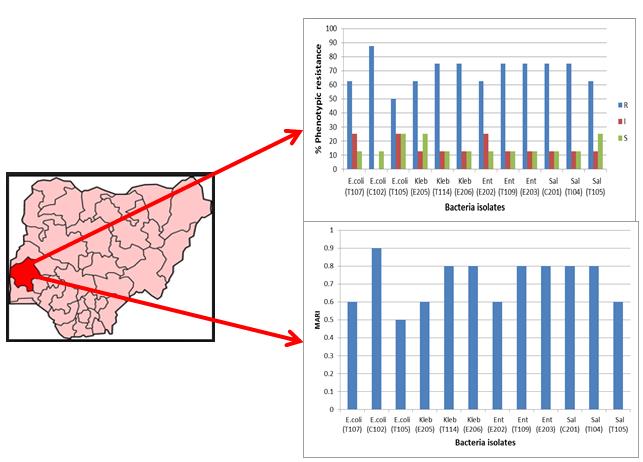
Fish currently provide 6.7% of all protein consumed by humans globally, nevertheless, aquaculture system has been linked to fish and environmental contamination and disease outbreak. This study aims to isolate, identify, and characterise, bacteria in fish and pond water as well as the antibiotic profile of detected Coliforms. The susceptibility of the isolates was tested using the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method on Mueller Hinton agar. A total of forty (40) isolates were isolated from the water samples of which (5) species were Gram Positive bacteria and 35 species of Gram Negative bacteria. The temperature for all ponds ranged from 25°C to 28°C. The mean bacteria count for pond C1 to T2 were 4.9 × 102, 4.9 × 102, 5.4 × 102, 2.5 × 102, 2.2 × 102, and 1.9 × 102 CFU/ml respectively. All isolates were 100% resistant to ceftazidime, cefuroxime and augmentin. More resistance to cefixime (80%) and gentamicin (73.3%) and nitrofurantoin (66.7%) was recorded. However, only 16.6% and 8.3% of the isolates were resistant to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin respectively. The multiple antimicrobial resistance index (MARI) ranged from 0.5 to 0.9. The water quality parameters (temperature and pH) and the type of bacteria detected in all pond type did not differ significantly. The Multi-drug resistance bacteria detected could be pathogenic to fish and consumers.