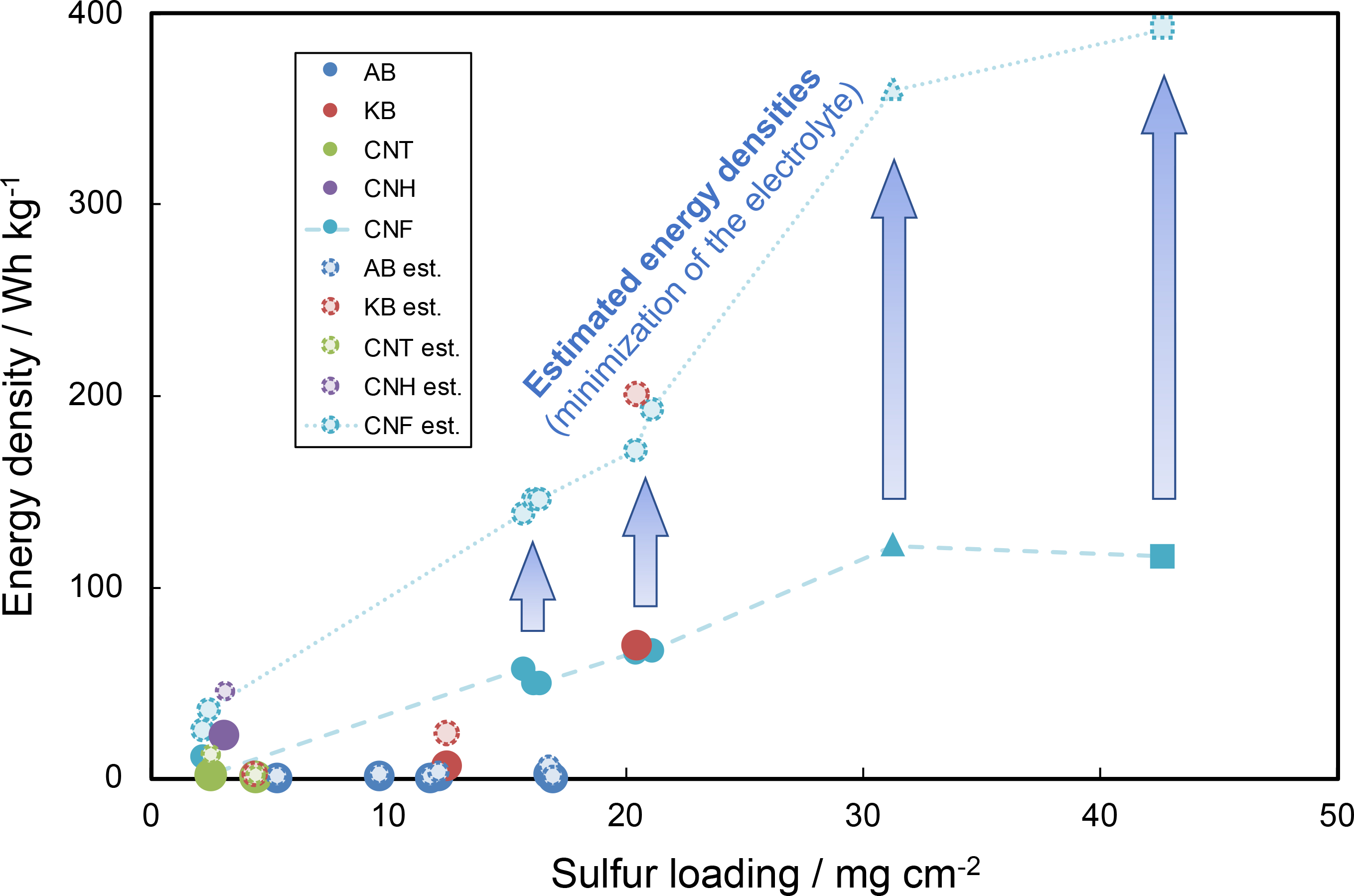
Various types of electroconductive additives were evaluated for high C-rate capability in an attempt to extend practical application of high-areal-capacity lithium–sulfur batteries that employ an aluminum-foam current collector. Carbon nanofibers (CNFs) were found to be the most effective additive, with the ability to attain a high-sulfur-loading of 40 mg cm−2. A CNF-containing cell exhibited gravimetric capacities of 1094 and 758 mAh gsulfur−1 (46.8 and 32.4 mAh cm−2) at 0.05 and 0.1 C-rate, respectively, in an ether-based electrolyte. Because a CNF-containing slurry exhibits low viscosity even at a high solid ratio, it could be filled into the aluminum foam. Additionally, a lithium–sulfur battery with high-sulfur-loading had an energy density of ~120 Wh kg−1, a value that was calculated from the weight of the components of the cathode, anode, current collectors, electrolyte, and separator. Assuming that the amount of electrolyte decreases and that the energy density of cells accumulate, a theoretical energy density of 522 Wh kg−1 was estimated. Moreover, it was found that even if a high-areal-capacity was achieved, the discharge capacity converged at a high C-rate, unless there was an improvement in ion diffusion in the bulk electrolyte. This is considered a limitation of sulfur cathodes with high-sulfur-loading.