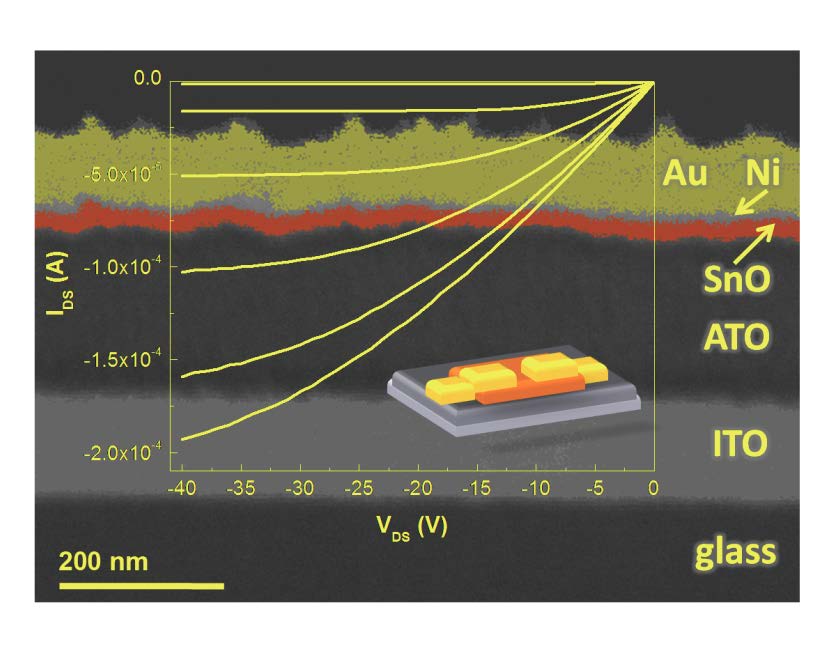
This work reports the role of structure and composition on the determination of the performances of p-type SnOx TFTs deposited by rf magnetron sputtering at room temperature, followed by a post-annealed step up to 200 °C at different oxygen partial pressures (Opp), between 0% and 20%, but where the p-type conduction was only observed between 2.8–3.8%. The role of structure and composition were evaluated by XRD and Mössbauer spectroscopic studies. The study allows to identify the best phases/compositions and thicknesses (around 12 nm) to be used that lead to the production of TFTs with a bottom gate configuration, on glasses coated with conductive Indium Tin Oxide, followed by Aluminium Titanium Oxide dielectric layer with saturation mobility of 4.6 cm2V−1s−1 and on-off ratio above 7 × 104, operating at the enhancement mode with a saturation voltage of −10 V.