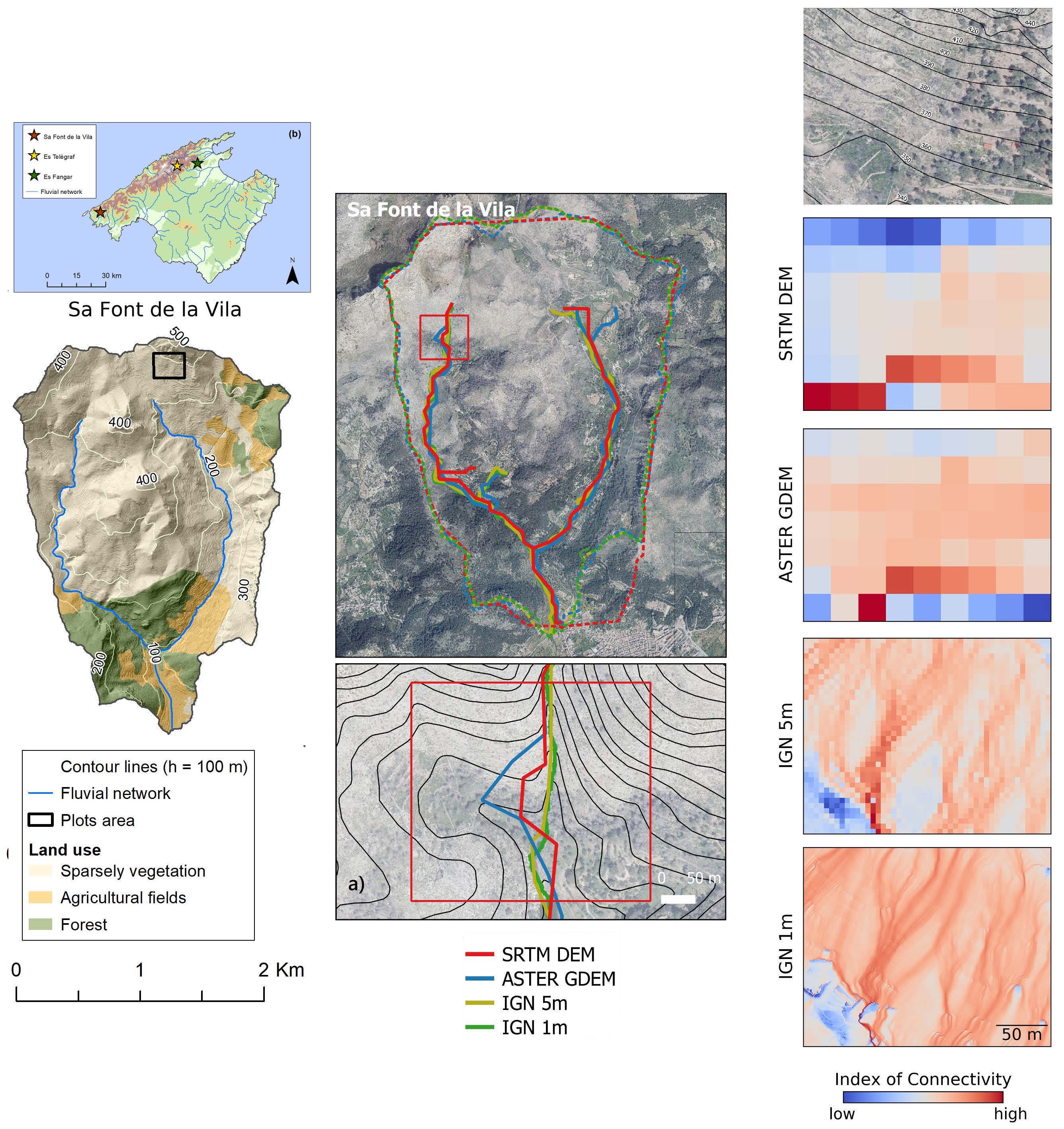
Digital Terrain Models (DTMs) are currently a fundamental source of information in Earth Sciences. However, DTM-based studies can contain remarkable biases if limitations and inaccuracies of these models are disregarded. In this work, four freely available datasets such as SRTM C-SAR DEM, ASTER GDEM V2 and two airborne LiDAR derived DTMs (at 5 and 1 m spatial resolution, respectively) were analysed in a comparative study in three geomorphologically contrasted catchments located in Mediterranean geoecosystems under intensive human land use influence. Vertical accuracy as well as the influence of each dataset characteristics on hydrological and geomorphological modelling applicability were assessed by using classic geometric and morphometric parameters and the more recently proposed index of sediment connectivity. Overall vertical accuracy – expressed as Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) and Normalized Median Deviation (NMAD) – revealed the highest accuracy in the cases of the 1 m (RMSE = 1.55 m; NMAD = 0.44 m) and 5 m LiDAR DTMs (RMSE = 1.73 m; NMAD = 0.84 m). Vertical accuracy of SRTM was lower (RMSE = 6.98 m; NMAD = 5.27 m) but considerably higher than in the case of ASTER (RMSE = 16.10 m; NMAD = 11.23 m). All datasets were affected by systematic distortions. As a consequence, propagation of these errors caused negative impacts on flow routing, stream network and catchment delineation and, to a lower extent, on the distribution of slope values. These limitations should be carefully considered when applying DTMs for hydrogeomorphological modelling.