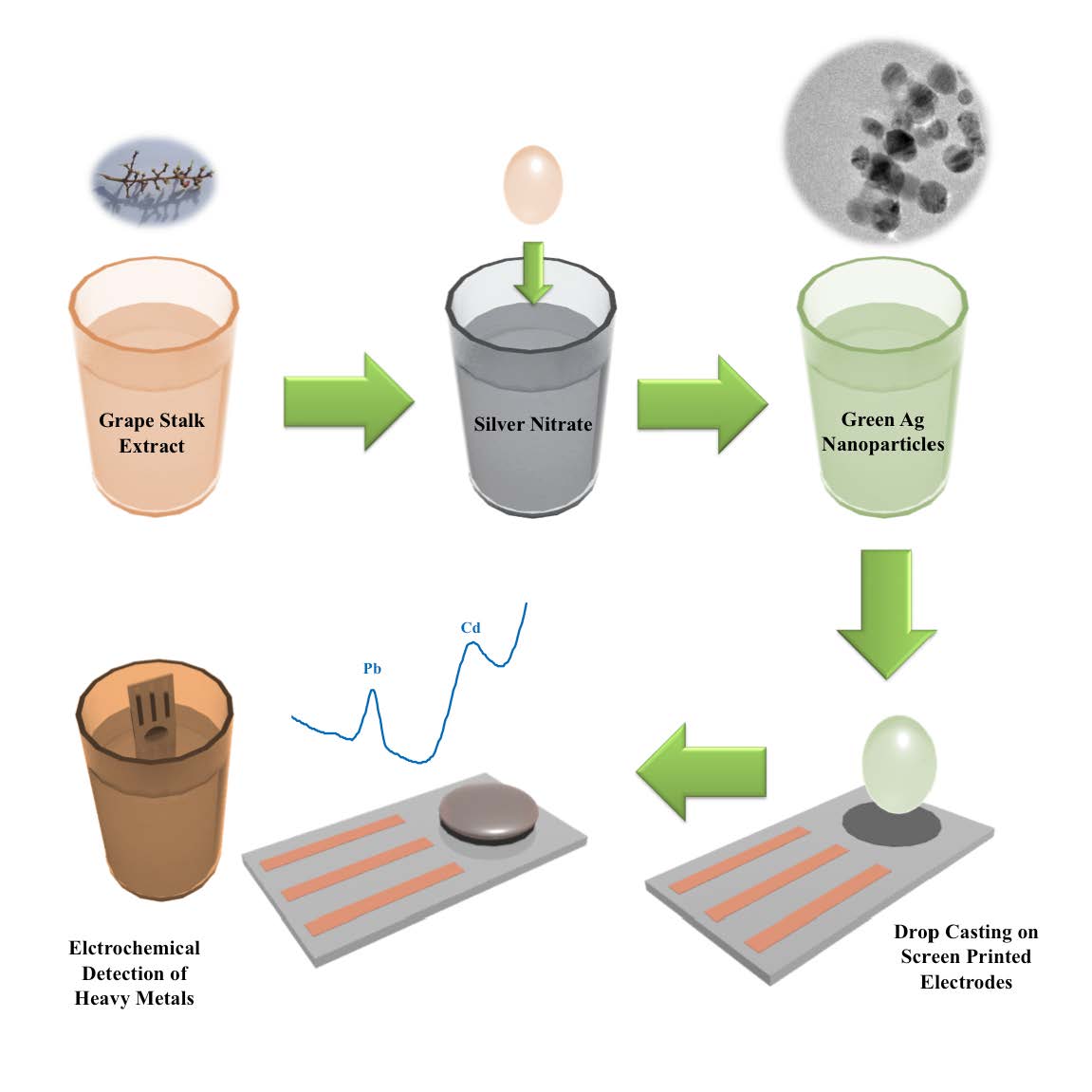
The chemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) by using an environmentally friendly methodology for their preparation is presented. Thus, considering that plants possess components that can act as reducing agents and stabilizers in the nanoparticles production, in this work, the synthesis of Ag-NPs by using a solution of grape waste extract as reducing and capping agent is studied. First, the total polyphenols content and reducing sugars in extracts produced at different conditions are characterized. After that, Ag-NPs are synthesized regarding the interaction of Ag ions (from silver nitrate) and the grape waste extract. The effect of temperature, contact time, extract/metal solution volume ratio and pH solution in the synthesis of metal nanoparticles are studied too. Different sets of nanoparticle samples are fully characterized by means of Electron Microscopy coupled with Energy Dispersive X-Ray for qualitative chemical identification. Ag-NPs with an average diameter of 27.7 ± 0.6 nm are selected to proof their suitability for sensing purposes. Thus, screen-printed electrodes modified with Ag-NPs are tested for the simultaneous voltammetric stripping determination of Pb(II) and Cd(II). Results indicate good reproducibility, sensitivity and limits of detection around 2.7 µg L−1 for both metal ions.