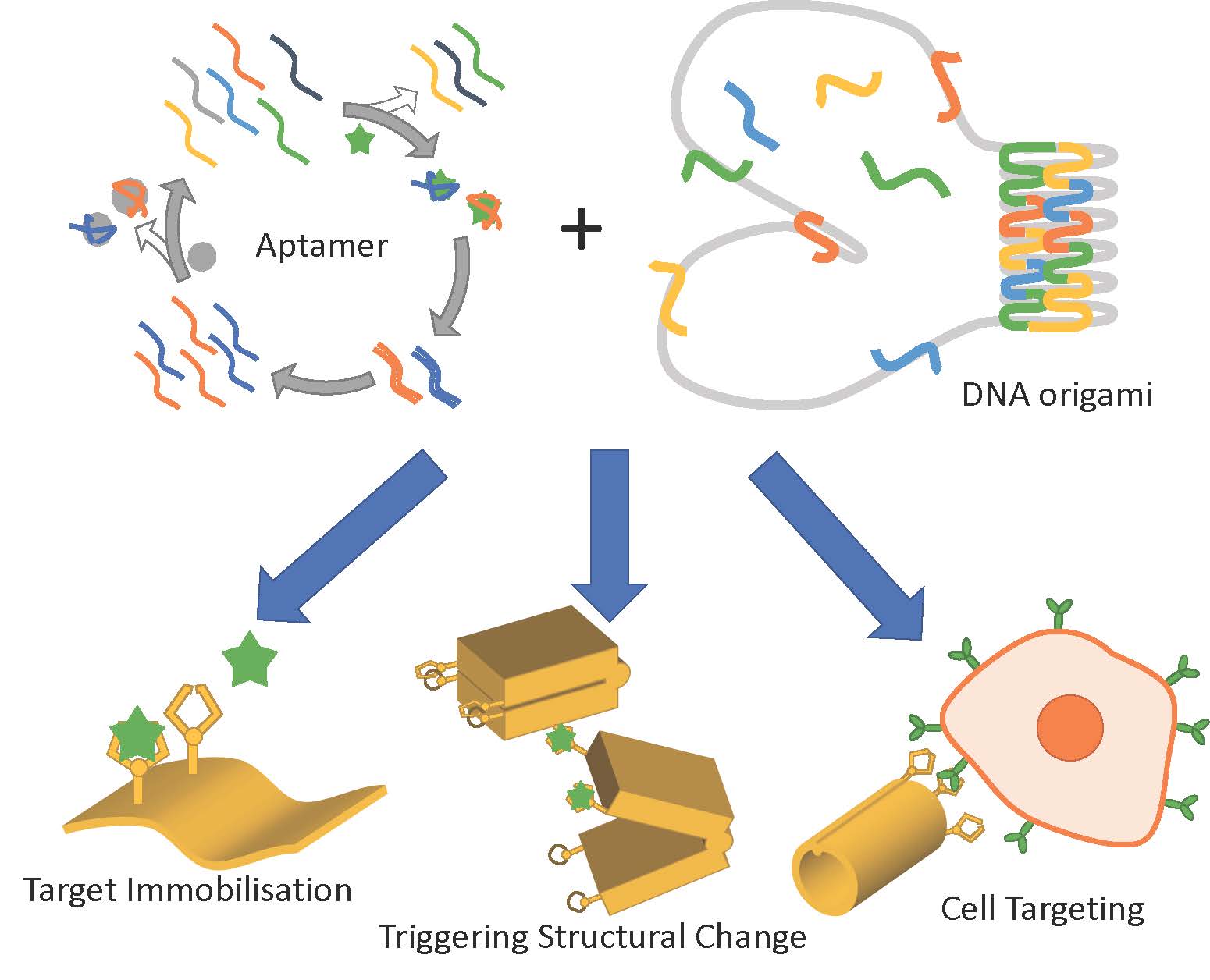
DNA origami has emerged in recent years as a powerful technique for designing and building 2D and 3D nanostructures. While the breadth of structures that have been produced is impressive, one of the remaining challenges, especially for DNA origami structures intended to carry out useful biomedical tasks in vivo, is to endow them with the ability to detect and respond to molecules of interest. Target molecules may be disease indicators or cell surface receptors, and the responses may include conformational changes leading to release of therapeutically relevant cargo. Nucleic acid aptamers are ideally suited to this task and are beginning to be used in DNA origami designs. In this review we consider examples of uses of DNA aptamers in DNA origami structures and summarise what is currently understood regarding aptamer-origami integration. We review three major roles for aptamers in such applications: protein immobilisation, triggering of structural transformation, and cell targeting. Finally, we consider future perspectives for DNA aptamer integration with DNA origami.