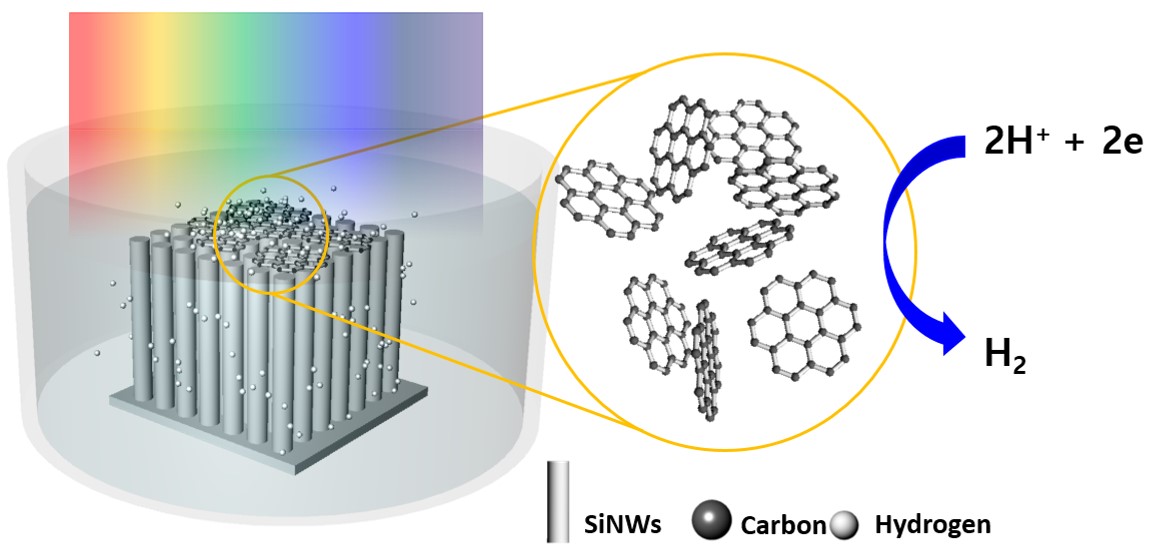
Silicon-based photoelectrochemical (PEC) conversion system has recently gained attention with its ability to provide cost-efficient and superior photoresponsive behavior in regard to other various semiconductor photoelectrodes. Carbon-based co-catalysts have always shared the spotlight for being rendered as alternative metal-free electrocatalysts intended for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). In particular, a representative carbon-derived material, reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) has attracted much attention as a non-metal catalyst for efficient and durable HER. Herein, we have deposited rGO on silicon nanowire (SiNW) structure which shows the highest reduction in the overpotential for HER up to date. This could be attributed to the synergistic effects of rGO and SiNW with unique anisotropic morphology, facile tuning capabilities, and scalable fabrication methods. Combined with nanostructured photocathode, rGO deposited SiNW showed better applied bias photon to current conversion efficiency of 3.16%, which is 158 times higher than that of bare planar Si system. In regard to this development we believe that rGO-SiNW photoelectrodes would pave the way for state-of-the-art highly efficient non-metal catalysts for energy conversion technologies.