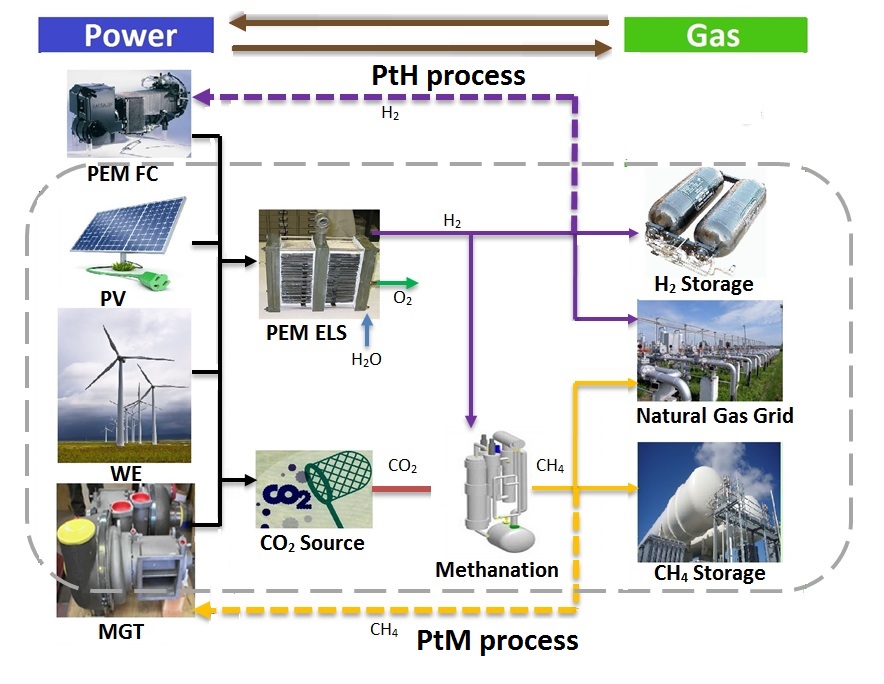
This paper deals with the techno-economic study of the hybrid renewable energy system based on energy storage aspect under the form of hydrogen and methane. Indeed, with the intermittency of the renewable energy sources such as photovoltaic and wind energy, several problems of produced energy injection to the power system network can be encountered due to the shortage or the excess of these sources. This situation appeals the use of systems that ensure the stability of network based on the storage of energy surplus into gas using electrolyzer systems, which will be used afterward to cover the eventual shortage. In the present paper, the study of performance of each pathway of methane and hydrogen storage has been performed by the treatment of multiple scenarios via different architecture case studies in an Algerian location. Whereas, the energy produced by the photovoltaic system, the wind energy and the gas micro turbine sources are considered similar in each case. The modeling and simulation of the studied system operation under optimization criteria has been performed in this work, where the main aim is to define the appropriate configuration taking into account the different with low costs of investment, maintenance operation and immediate reactivity with a big storage capacity.