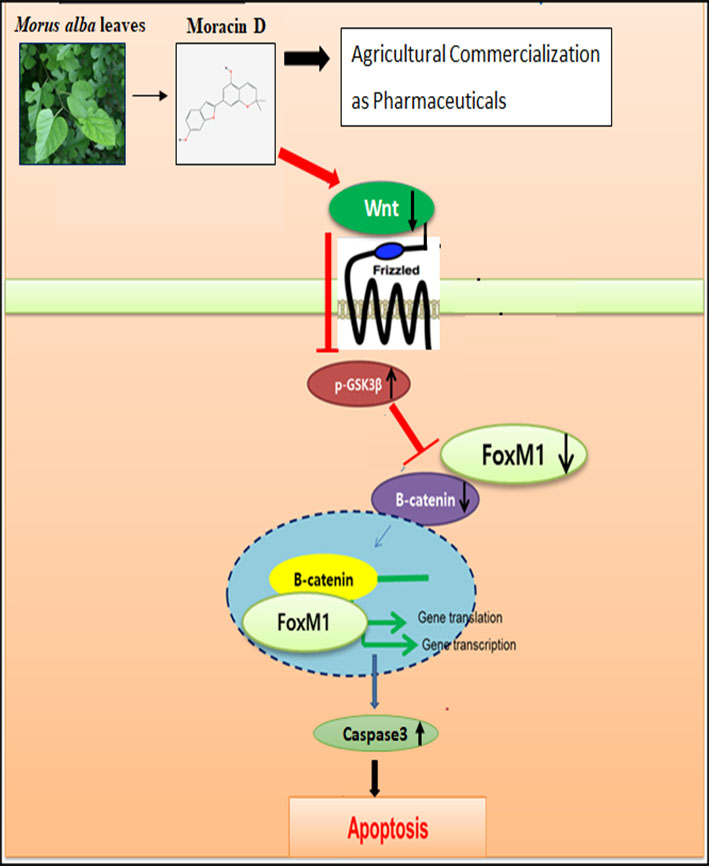
Though Moracin D derived from Morus alba was known to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, the underlying antitumor mechanism of Moracin D was never unveiled so far. Thus, in the recent study, the apoptotic mechanism of Moracin D was elucidated in breast cancer cells. Herein, Moracin D exerted significant cytotoxicity in MDA-MB231 and MCF7 cells. Also, Moracin D increased sub G1 population, cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and attenuated the expression of pro-cysteine aspartyl-specific protease (procaspase 3), c-Myc, cyclin D1, B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2),and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) in MDA-MB231 cells. Of note, Moracin D reduced expression of Forkhead box M1 (FOXM1), β-catenin, Wnt3a, and upregulated glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK 3β) on Tyr216 along with disturbed binding of FOXM1 with β-catenin in MDA-MB-231 cells. Conversely, GSK3β inhibitor SB216763 reversed the apoptotic ability of Moracin D to reduce expression of FOXM1, β-catenin, pro-caspase3 and pro-PARP in MDA-MB-231 cells. Overall, these findings provide novel insight that Moracin D inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis via suppression of Wnt3a/FOXM1/β-catenin signaling and activation of caspase and GSK3β