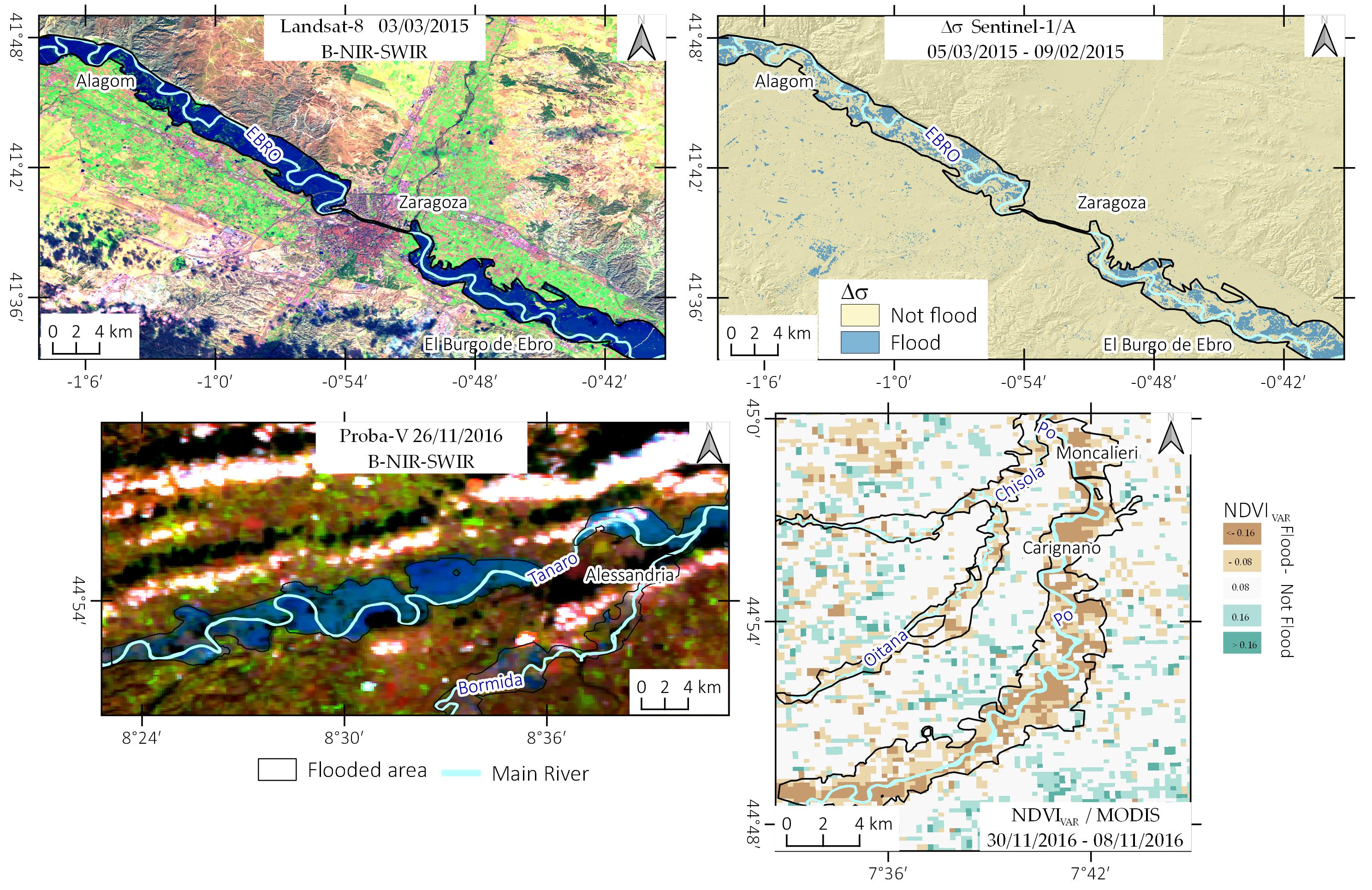
Satellite remote sensing is a powerful tool to map flooded areas. In the last years, the availability of free satellite data sensibly increased in terms of type and frequency, allowing producing flood maps at low cost around the World. In this work, we propose a semi-automatic method for flood mapping, based only on free satellite images and open-source software. As case studies, we selected three flood events recently occurred in Spain and Italy. Multispectral satellite data acquired by MODIS, Proba-V, Landsat, Sentinel-2 and SAR data collected by Sentinel-1 were used to detect flooded areas using different methodologies (e.g., MNDWI; SAR backscattering variation; Supervised classification). Then, we improved and manually refined the automatic mapping using free ancillary data like DEM based water depth model and available ground truth data. For the areas affected by major floods, we also validated and compared the produced flood maps with official maps made by river authorities. We calculated flood detection performance (flood ratio) for the different datasets we used. The results show that it is necessary to take into account different factors for the choice of best satellite data, among these, the time of satellite pass with respect to the flood peak is the most important one. SAR data showed good results only for co-flood acquisitions, whereas multispectral images allowed detecting flooded areas also with the post-flood acquisition. With the support of ancillary data, it was possible to produce reliable geomorphological based flood maps in the study areas.