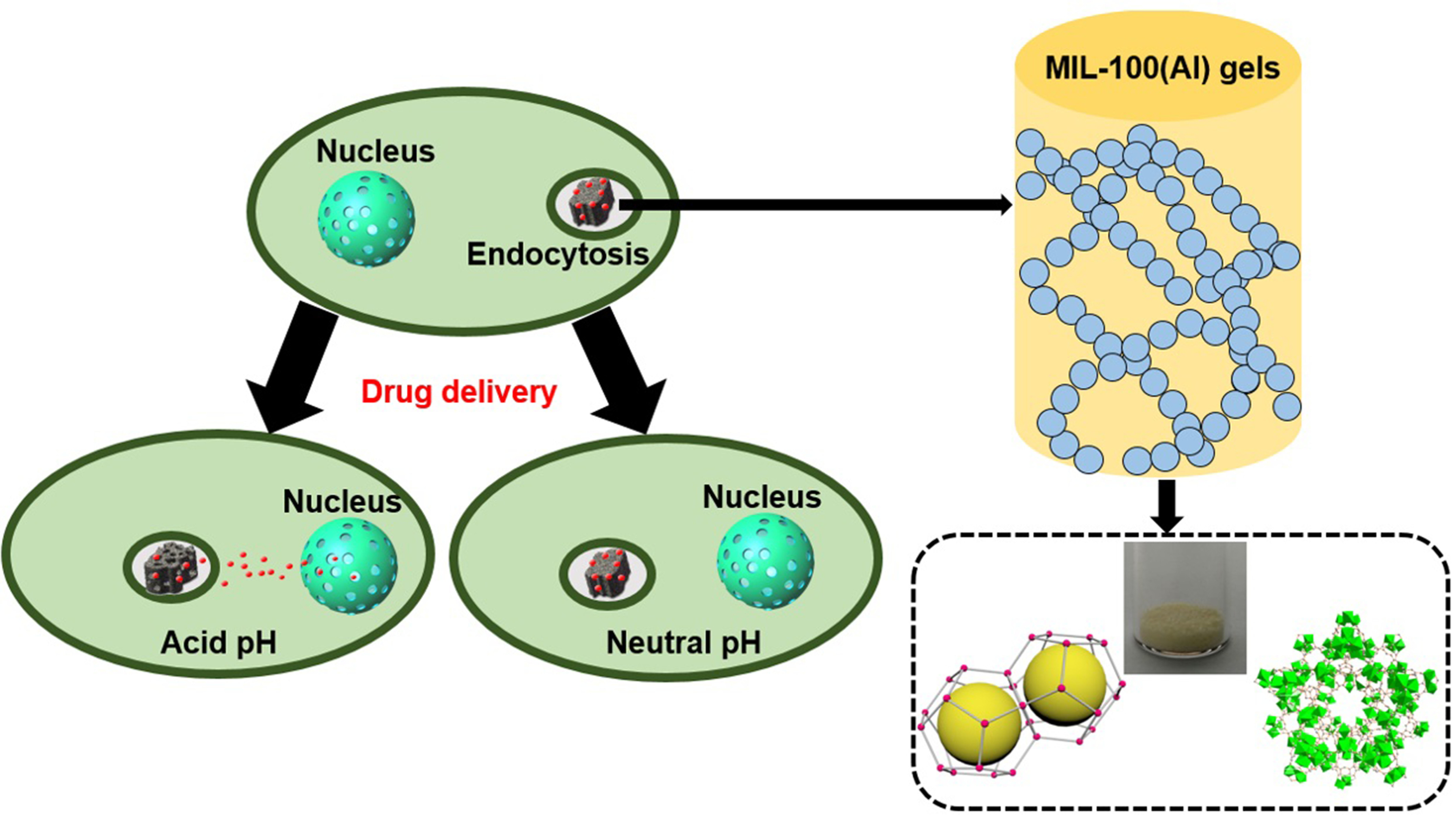
Slow and controlled release systems for drugs, have attracted increasing interest recently. A highly efficient metal-organic gels (MOGs) drug delivery carrier, i.e., MIL-100(Al) gels, has been fabricated by a facile, low cost and environment friendly one-pot process. The unique structure of MIL-100(Al) gels leads to a high loading efficiency (620 mg/g) towards doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) as a kind of anticancer drugs. DOX-loaded MOGs exhibited high stability under physiological conditions and sustained release capacity of DOX for up to 3 days (under acidic environments). They further showed sustained drug release behavior and excellent antitumor effects in in vitro experiments on HeLa cells, in contrast with the extremely low biotoxicity of MOGs. Our work provides a promising way for the anticancer therapy, by utilizing this MOGs-based drug delivery system, as an efficient and safe vehicle.