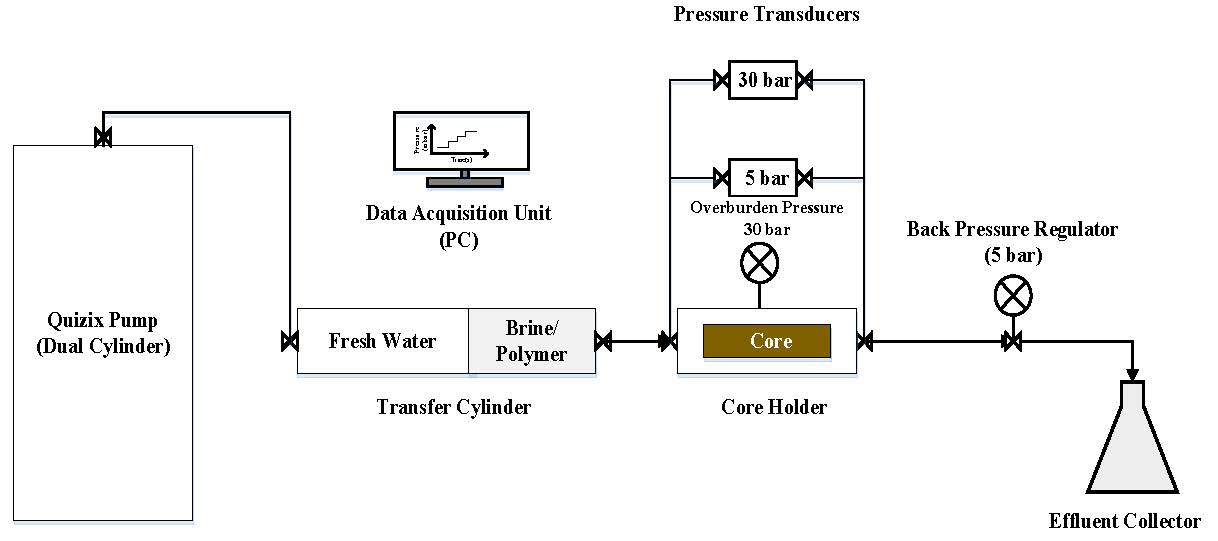
Polymer flooding is an established enhanced oil recovery (EOR) method, still many aspects of polymer flooding are not well understood. This study investigates the influence of mechanical degradation on flow properties of polymers in porous media. Mechanical degradation due to high shear forces may occur in the injection well and at the entrance to the porous media. The polymers that give high viscosity yields at a sustainable economic cost are typically large, MW > 10 MDa, and have wide molecular weight distributions. Both MW and the distributions are altered by mechanical degradation, leading to changes in the flow rheology of the polymer. The polymer solutions were subjected to different degrees of pre-shearing and pre-filtering before injected into Bentheimer outcrop sandstone cores. Rheology studies of injected and produced polymer solutions were performed and interpreted together with in-situ rheology data. The core floods showed a predominant shear thickening behavior at high flow velocities which is due to successive contraction/expansion flow in pores. When pre-sheared, shear thickening was reduced but with no significant reduction in in-situ viscosity at lower flow rates. This may be explained by reduction in the extensional viscosity. Furthermore, the results show that successive degradation occurred which suggests that the assumption of the highest point of shear which determines mechanical degradation in a porous media does not hold for all field relevant conditions.