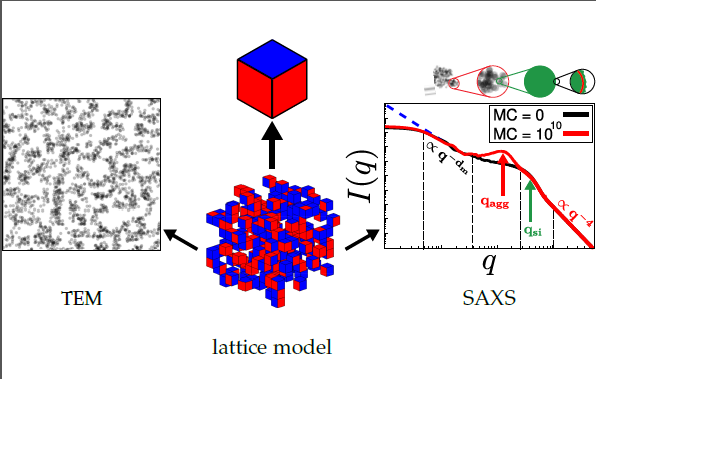
The properties of rubber are strongly influenced by the distribution of filler within the polymer matrix. Here we introduce a Monte Carlo-based morphology generator. The basic elements of our model are cubic cells, which, in the current version, can be either silica filler particles or rubber volume elements in adjustable proportion. The model allows the assignment of surface free energies to the particles according to whether a surface represents, for instance, 'naked' silica or silanised silica. The amount of silanisation is variable. We use a nearest-neighbour site-exchange Monte Carlo algorithm to generate filler morphologies, mimicking flocculation. Transmission electron micrographs (TEM) as well as small angle scattering (SAS) intensities can be calculated along the Monte Carlo trajectory. In this work we demonstrate the application of our morphology generator in terms of selected examples. We illustrate its potential as a tool for screening studies, relating interface tensions between the components to filler network structure as characterized by TEM and SAS.